diff --git a/docs/source/zh/_toctree.yml b/docs/source/zh/_toctree.yml
index 6416c468a8e9..2d02be911f54 100644
--- a/docs/source/zh/_toctree.yml
+++ b/docs/source/zh/_toctree.yml
@@ -1,12 +1,73 @@
-- sections:
+- title: 开始Diffusers
+ sections:
- local: index
- title: 🧨 Diffusers
+ title: Diffusers
+ - local: installation
+ title: 安装
- local: quicktour
title: 快速入门
- local: stable_diffusion
title: 有效和高效的扩散
- - local: consisid
- title: 身份保持的文本到视频生成
- - local: installation
- title: 安装
- title: 开始
+
+- title: DiffusionPipeline
+ isExpanded: false
+ sections:
+ - local: using-diffusers/schedulers
+ title: Load schedulers and models
+
+- title: Inference optimization
+ isExpanded: false
+ sections:
+ - local: optimization/fp16
+ title: Accelerate inference
+ - title: Community optimizations
+ sections:
+ - local: optimization/xformers
+ title: xFormers
+
+
+- title: Training
+ isExpanded: false
+ sections:
+ - local: training/overview
+ title: Overview
+ - local: training/adapt_a_model
+ title: Adapt a model to a new task
+ - title: Models
+ sections:
+ - local: training/text2image
+ title: Text-to-image
+ - local: training/controlnet
+ title: ControlNet
+ - title: Methods
+ sections:
+ - local: training/text_inversion
+ title: Textual Inversion
+ - local: training/lora
+ title: LoRA
+
+- title: Model accelerators and hardware
+ isExpanded: false
+ sections:
+ - local: optimization/onnx
+ title: ONNX
+
+- title: Specific pipeline examples
+ isExpanded: false
+ sections:
+ - local: using-diffusers/consisid
+ title: ConsisID
+
+- title: Resources
+ isExpanded: false
+ sections:
+ - title: Task recipes
+ sections:
+ - local: conceptual/philosophy
+ title: Philosophy
+ - local: conceptual/contribution
+ title: How to contribute?
+ - local: conceptual/ethical_guidelines
+ title: Diffusers' Ethical Guidelines
+ - local: conceptual/evaluation
+ title: Evaluating Diffusion Models
diff --git a/docs/source/zh/conceptual/contribution.md b/docs/source/zh/conceptual/contribution.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000000..0f9743882523
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/source/zh/conceptual/contribution.md
@@ -0,0 +1,485 @@
+
+
+# 如何为Diffusers 🧨做贡献
+
+我们❤️来自开源社区的贡献!欢迎所有人参与,所有类型的贡献——不仅仅是代码——都受到重视和赞赏。回答问题、帮助他人、主动交流以及改进文档对社区都极具价值,所以如果您愿意参与,请不要犹豫!
+
+我们鼓励每个人先在公开Discord频道里打招呼👋。在那里我们讨论扩散模型的最新趋势、提出问题、展示个人项目、互相协助贡献,或者只是闲聊☕。 +
+无论您选择以何种方式贡献,我们都致力于成为一个开放、友好、善良的社区。请阅读我们的[行为准则](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md),并在互动时注意遵守。我们也建议您了解指导本项目的[伦理准则](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/conceptual/ethical_guidelines),并请您遵循同样的透明度和责任原则。
+
+我们高度重视社区的反馈,所以如果您认为自己有能帮助改进库的有价值反馈,请不要犹豫说出来——每条消息、评论、issue和拉取请求(PR)都会被阅读和考虑。
+
+## 概述
+
+您可以通过多种方式做出贡献,从在issue和讨论区回答问题,到向核心库添加新的diffusion模型。
+
+下面我们按难度升序列出不同的贡献方式,所有方式对社区都很有价值:
+
+* 1. 在[Diffusers讨论论坛](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers)或[Discord](https://discord.gg/G7tWnz98XR)上提问和回答问题
+* 2. 在[GitHub Issues标签页](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new/choose)提交新issue,或在[GitHub Discussions标签页](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/discussions/new/choose)发起新讨论
+* 3. 在[GitHub Issues标签页](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues)解答issue,或在[GitHub Discussions标签页](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/discussions)参与讨论
+* 4. 解决标记为"Good first issue"的简单问题,详见[此处](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22good+first+issue%22)
+* 5. 参与[文档](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/docs/source)建设
+* 6. 贡献[社区Pipeline](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3Acommunity-examples)
+* 7. 完善[示例代码](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples)
+* 8. 解决标记为"Good second issue"的中等难度问题,详见[此处](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22Good+second+issue%22)
+* 9. 添加新pipeline/模型/调度器,参见["New Pipeline/Model"](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22New+pipeline%2Fmodel%22)和["New scheduler"](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22New+scheduler%22)类issue。此类贡献请先阅读[设计哲学](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/PHILOSOPHY.md)
+
+重申:**所有贡献对社区都具有重要价值。**下文将详细说明各类贡献方式。
+
+对于4-9类贡献,您需要提交PR(拉取请求),具体操作详见[如何提交PR](#how-to-open-a-pr)章节。
+
+### 1. 在Diffusers讨论区或Discord提问与解答
+
+任何与Diffusers库相关的问题或讨论都可以发布在[官方论坛](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers/)或[Discord频道](https://discord.gg/G7tWnz98XR),包括但不限于:
+- 分享训练/推理实验报告
+- 展示个人项目
+- 咨询非官方训练示例
+- 项目提案
+- 通用反馈
+- 论文解读
+- 基于Diffusers库的个人项目求助
+- 一般性问题
+- 关于diffusion模型的伦理讨论
+- ...
+
+论坛/Discord上的每个问题都能促使社区公开分享知识,很可能帮助未来遇到相同问题的初学者。请务必提出您的疑问。
+同样地,通过回答问题您也在为社区创造公共知识文档,这种贡献极具价值。
+
+**请注意**:提问/回答时投入的精力越多,产生的公共知识质量就越高。精心构建的问题与专业解答能形成高质量知识库,而表述不清的问题则可能降低讨论价值。
+
+低质量的问题或回答会降低公共知识库的整体质量。
+简而言之,高质量的问题或回答应具备*精确性*、*简洁性*、*相关性*、*易于理解*、*可访问性*和*格式规范/表述清晰*等特质。更多详情请参阅[如何提交优质议题](#how-to-write-a-good-issue)章节。
+
+**关于渠道的说明**:
+[*论坛*](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers/63)的内容能被谷歌等搜索引擎更好地收录,且帖子按热度而非时间排序,便于查找历史问答。此外,论坛内容更容易被直接链接引用。
+而*Discord*采用即时聊天模式,适合快速交流。虽然在Discord上可能更快获得解答,但信息会随时间淹没,且难以回溯历史讨论。因此我们强烈建议在论坛发布优质问答,以构建可持续的社区知识库。若Discord讨论产生有价值结论,建议将成果整理发布至论坛以惠及更多读者。
+
+### 2. 在GitHub议题页提交新议题
+
+🧨 Diffusers库的稳健性离不开用户的问题反馈,感谢您的报错。
+
+请注意:GitHub议题仅限处理与Diffusers库代码直接相关的技术问题、错误报告、功能请求或库设计反馈。
+简言之,**与Diffusers库代码(含文档)无关**的内容应发布至[论坛](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers/63)或[Discord](https://discord.gg/G7tWnz98XR)。
+
+**提交新议题时请遵循以下准则**:
+- 确认是否已有类似议题(使用GitHub议题页的搜索栏)
+- 请勿在现有议题下追加新问题。若存在高度关联议题,应新建议题并添加相关链接
+- 确保使用英文提交。非英语用户可通过[DeepL](https://www.deepl.com/translator)等免费工具翻译
+- 检查升级至最新Diffusers版本是否能解决问题。提交前请确认`python -c "import diffusers; print(diffusers.__version__)"`显示的版本号不低于最新版本
+- 记请记住,你在提交新issue时投入的精力越多,得到的回答质量就越高,Diffusers项目的整体issue质量也会越好。
+
+新issue通常包含以下内容:
+
+#### 2.1 可复现的最小化错误报告
+
+错误报告应始终包含可复现的代码片段,并尽可能简洁明了。具体而言:
+- 尽量缩小问题范围,**不要直接粘贴整个代码文件**
+- 规范代码格式
+- 除Diffusers依赖库外,不要包含其他外部库
+- **务必**提供环境信息:可在终端运行`diffusers-cli env`命令,然后将显示的信息复制到issue中
+- 详细说明问题。如果读者不清楚问题所在及其影响,就无法解决问题
+- **确保**读者能以最小成本复现问题。如果代码片段因缺少库或未定义变量而无法运行,读者将无法提供帮助。请确保提供的可复现代码尽可能精简,可直接复制到Python shell运行
+- 如需特定模型/数据集复现问题,请确保读者能获取这些资源。可将模型/数据集上传至[Hub](https://huggingface.co)便于下载。尽量保持模型和数据集体积最小化,降低复现难度
+
+更多信息请参阅[如何撰写优质issue](#how-to-write-a-good-issue)章节。
+
+提交错误报告请点击[此处](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=bug&projects=&template=bug-report.yml)。
+
+#### 2.2 功能请求
+
+优质的功能请求应包含以下要素:
+
+1. 首先说明动机:
+* 是否与库的使用痛点相关?若是,请解释原因,最好提供演示问题的代码片段
+* 是否因项目需求产生?我们很乐意了解详情!
+* 是否是你已实现且认为对社区有价值的功能?请说明它为你解决了什么问题
+2. 用**完整段落**描述功能特性
+3. 提供**代码片段**演示预期用法
+4. 如涉及论文,请附上链接
+5. 可补充任何有助于理解的辅助材料(示意图、截图等)
+
+提交功能请求请点击[此处](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=&template=feature_request.md&title=)。
+
+#### 2.3 设计反馈
+
+关于库设计的反馈(无论正面还是负面)能极大帮助核心维护者打造更友好的库。要了解当前设计理念,请参阅[此文档](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/conceptual/philosophy)如果您认为某个设计选择与当前理念不符,请说明原因及改进建议。如果某个设计选择因过度遵循理念而限制了使用场景,也请解释原因并提出调整方案。
+若某个设计对您特别实用,请同样留下备注——这对未来的设计决策极具参考价值。
+
+您可通过[此链接](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=&template=feedback.md&title=)提交设计反馈。
+
+#### 2.4 技术问题
+
+技术问题主要涉及库代码的实现逻辑或特定功能模块的作用。提问时请务必:
+- 附上相关代码链接
+- 详细说明难以理解的具体原因
+
+技术问题提交入口:[点击此处](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=bug&template=bug-report.yml)
+
+#### 2.5 新模型/调度器/pipeline提案
+
+若diffusion模型社区发布了您希望集成到Diffusers库的新模型、pipeline或调度器,请提供以下信息:
+* 简要说明并附论文或发布链接
+* 开源实现链接(如有)
+* 模型权重下载链接(如已公开)
+
+若您愿意参与开发,请告知我们以便指导。另请尝试通过GitHub账号标记原始组件作者。
+
+提案提交地址:[新建请求](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=New+model%2Fpipeline%2Fscheduler&template=new-model-addition.yml)
+
+### 3. 解答GitHub问题
+
+回答GitHub问题可能需要Diffusers的技术知识,但我们鼓励所有人尝试参与——即使您对答案不完全正确。高质量回答的建议:
+- 保持简洁精炼
+- 严格聚焦问题本身
+- 提供代码/论文等佐证材料
+- 优先用代码说话:若代码片段能解决问题,请提供完整可复现代码
+
+许多问题可能存在离题、重复或无关情况。您可以通过以下方式协助维护者:
+- 引导提问者精确描述问题
+- 标记重复issue并附原链接
+- 推荐用户至[论坛](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers/63)或[Discord](https://discord.gg/G7tWnz98XR)
+
+在确认提交的Bug报告正确且需要修改源代码后,请继续阅读以下章节内容。
+
+以下所有贡献都需要提交PR(拉取请求)。具体操作步骤详见[如何提交PR](#how-to-open-a-pr)章节。
+
+### 4. 修复"Good first issue"类问题
+
+标有[Good first issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22good+first+issue%22)标签的问题通常已说明解决方案建议,便于修复。若该问题尚未关闭且您想尝试解决,只需留言"我想尝试解决这个问题"。通常有三种情况:
+- a.) 问题描述已提出解决方案。若您认可该方案,可直接提交PR或草稿PR进行修复
+- b.) 问题描述未提出解决方案。您可询问修复建议,Diffusers团队会尽快回复。若有成熟解决方案,也可直接提交PR
+- c.) 已有PR但问题未关闭。若原PR停滞,可新开PR并关联原PR(开源社区常见现象)。若PR仍活跃,您可通过建议、审查或协作等方式帮助原作者
+
+### 5. 文档贡献
+
+优秀库**必然**拥有优秀文档!官方文档是新用户的首要接触点,因此文档贡献具有**极高价值**。贡献形式包括:
+- 修正拼写/语法错误
+- 修复文档字符串格式错误(如显示异常或链接失效)
+- 修正文档字符串中张量的形状/维度描述
+- 优化晦涩或错误的说明
+- 更新过时代码示例
+- 文档翻译
+
+[官方文档页面](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/index)所有内容均属可修改范围,对应[文档源文件](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/docs/source)可进行编辑。修改前请查阅[验证说明](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/docs)。
+
+### 6. 贡献社区流程
+
+> [!TIP]
+> 阅读[社区流程](../using-diffusers/custom_pipeline_overview#community-pipelines)指南了解GitHub与Hugging Face Hub社区流程的区别。若想了解我们设立社区流程的原因,请查看GitHub Issue [#841](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/841)(简而言之,我们无法维护diffusion模型所有可能的推理使用方式,但也不希望限制社区构建这些流程)。
+
+贡献社区流程是向社区分享创意与成果的绝佳方式。您可以在[`DiffusionPipeline`]基础上构建流程,任何人都能通过设置`custom_pipeline`参数加载使用。本节将指导您创建一个简单的"单步"流程——UNet仅执行单次前向传播并调用调度器一次。
+
+1. 为社区流程创建one_step_unet.py文件。只要用户已安装相关包,该文件可包含任意所需包。确保仅有一个继承自[`DiffusionPipeline`]的流程类,用于从Hub加载模型权重和调度器配置。在`__init__`函数中添加UNet和调度器。
+
+ 同时添加`register_modules`函数,确保您的流程及其组件可通过[`~DiffusionPipeline.save_pretrained`]保存。
+
+```py
+from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
+import torch
+
+class UnetSchedulerOneForwardPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
+ def __init__(self, unet, scheduler):
+ super().__init__()
+
+ self.register_modules(unet=unet, scheduler=scheduler)
+```
+
+2. 在前向传播中(建议定义为`__call__`),可添加任意功能。对于"单步"流程,创建随机图像并通过设置`timestep=1`调用UNet和调度器一次。
+
+```py
+ from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
+ import torch
+
+ class UnetSchedulerOneForwardPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
+ def __init__(self, unet, scheduler):
+ super().__init__()
+
+ self.register_modules(unet=unet, scheduler=scheduler)
+
+ def __call__(self):
+ image = torch.randn(
+ (1, self.unet.config.in_channels, self.unet.config.sample_size, self.unet.config.sample_size),
+ )
+ timestep = 1
+
+ model_output = self.unet(image, timestep).sample
+ scheduler_output = self.scheduler.step(model_output, timestep, image).prev_sample
+
+ return scheduler_output
+```
+
+现在您可以通过传入UNet和调度器来运行流程,若流程结构相同也可加载预训练权重。
+
+```python
+from diffusers import DDPMScheduler, UNet2DModel
+
+scheduler = DDPMScheduler()
+unet = UNet2DModel()
+
+pipeline = UnetSchedulerOneForwardPipeline(unet=unet, scheduler=scheduler)
+output = pipeline()
+# 加载预训练权重
+pipeline = UnetSchedulerOneForwardPipeline.from_pretrained("google/ddpm-cifar10-32", use_safetensors=True)
+output = pipeline()
+```
+
+您可以选择将pipeline作为GitHub社区pipeline或Hub社区pipeline进行分享。
+
+
+
+
+通过向Diffusers[代码库](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers)提交拉取请求来分享GitHub pipeline,将one_step_unet.py文件添加到[examples/community](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/community)子文件夹中。
+
+
+
+
+通过在Hub上创建模型仓库并上传one_step_unet.py文件来分享Hub pipeline。
+
+
+
+
+### 7. 贡献训练示例
+
+Diffusers训练示例是位于[examples](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples)目录下的训练脚本集合。
+
+我们支持两种类型的训练示例:
+
+- 官方训练示例
+- 研究型训练示例
+
+研究型训练示例位于[examples/research_projects](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/research_projects),而官方训练示例包含[examples](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples)目录下除`research_projects`和`community`外的所有文件夹。
+官方训练示例由Diffusers核心维护者维护,研究型训练示例则由社区维护。
+这与[6. 贡献社区pipeline](#6-contribute-a-community-pipeline)中关于官方pipeline与社区pipeline的原因相同:核心维护者不可能维护diffusion模型的所有可能训练方法。
+如果Diffusers核心维护者和社区认为某种训练范式过于实验性或不够普及,相应训练代码应放入`research_projects`文件夹并由作者维护。
+
+官方训练和研究型示例都包含一个目录,其中含有一个或多个训练脚本、`requirements.txt`文件和`README.md`文件。用户使用时需要先克隆代码库:
+
+```bash
+git clone https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers
+```
+
+并安装训练所需的所有额外依赖:
+
+```bash
+cd diffusers
+pip install -r examples//requirements.txt
+```
+
+因此添加示例时,`requirements.txt`文件应定义训练示例所需的所有pip依赖项,安装完成后用户即可运行示例训练脚本。可参考[DreamBooth的requirements.txt文件](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/examples/dreambooth/requirements.txt)。
+- 运行示例所需的所有代码应集中在单个Python文件中
+- 用户应能通过命令行`python .py --args`直接运行示例
+- **示例**应保持简洁,主要展示如何使用Diffusers进行训练。示例脚本的目的**不是**创建最先进的diffusion模型,而是复现已知训练方案,避免添加过多自定义逻辑。因此,这些示例也力求成为优质的教学材料。
+
+提交示例时,强烈建议参考现有示例(如[dreambooth](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/examples/dreambooth/train_dreambooth.py))来了解规范格式。
+我们强烈建议贡献者使用[Accelerate库](https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate),因其与Diffusers深度集成。
+当示例脚本完成后,请确保添加详细的`README.md`说明使用方法,包括:
+- 运行示例的具体命令(示例参见[此处](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/dreambooth#running-locally-with-pytorch))
+- 训练结果链接(日志/模型等),展示用户可预期的效果(示例参见[此处](https://api.wandb.ai/report/patrickvonplaten/xm6cd5q5))
+- 若添加非官方/研究性训练示例,**必须注明**维护者信息(含Git账号),格式参照[此处](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/research_projects/intel_opts#diffusers-examples-with-intel-optimizations)
+
+贡献官方训练示例时,还需在对应目录添加测试文件(如[examples/dreambooth/test_dreambooth.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/examples/dreambooth/test_dreambooth.py)),非官方示例无需此步骤。
+
+### 8. 处理"Good second issue"类问题
+
+标有[Good second issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22Good+second+issue%22)标签的问题通常比[Good first issues](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22good+first+issue%22)更复杂。
+这类问题的描述通常不会提供详细解决指引,需要贡献者对库有较深理解。
+若您想解决此类问题,可直接提交PR并关联对应issue。若已有未合并的PR,请分析原因后提交改进版。需注意,Good second issue类PR的合并难度通常高于good first issues。在需要帮助的时候请不要犹豫,大胆的向核心维护者询问。
+
+### 9. 添加管道、模型和调度器
+
+管道(pipelines)、模型(models)和调度器(schedulers)是Diffusers库中最重要的组成部分。它们提供了对最先进diffusion技术的便捷访问,使得社区能够构建强大的生成式AI应用。
+
+通过添加新的模型、管道或调度器,您可能为依赖Diffusers的任何用户界面开启全新的强大用例,这对整个生成式AI生态系统具有巨大价值。
+
+Diffusers针对这三类组件都有一些开放的功能请求——如果您还不确定要添加哪个具体组件,可以浏览以下链接:
+- [模型或管道](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22New+pipeline%2Fmodel%22)
+- [调度器](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22New+scheduler%22)
+
+在添加任何组件之前,强烈建议您阅读[设计哲学指南](philosophy),以更好地理解这三类组件的设计理念。请注意,如果添加的模型、调度器或管道与我们的设计理念存在严重分歧,我们将无法合并,因为这会导致API不一致。如果您从根本上不同意某个设计选择,请改为提交[反馈问题](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=&template=feedback.md&title=),以便讨论是否应该更改库中的特定设计模式/选择,以及是否更新我们的设计哲学。保持库内的一致性对我们非常重要。
+
+请确保在PR中添加原始代码库/论文的链接,并最好直接在PR中@原始作者,以便他们可以跟踪进展并在有疑问时提供帮助。
+
+如果您在PR过程中遇到不确定或卡住的情况,请随时留言请求初步审查或帮助。
+
+#### 复制机制(Copied from)
+
+在添加任何管道、模型或调度器代码时,理解`# Copied from`机制是独特且重要的。您会在整个Diffusers代码库中看到这种机制,我们使用它的原因是为了保持代码库易于理解和维护。用`# Copied from`机制标记代码会强制标记的代码与复制来源的代码完全相同。这使得每当您运行`make fix-copies`时,可以轻松更新并将更改传播到多个文件。
+
+例如,在下面的代码示例中,[`~diffusers.pipelines.stable_diffusion.StableDiffusionPipelineOutput`]是原始代码,而`AltDiffusionPipelineOutput`使用`# Copied from`机制来复制它。唯一的区别是将类前缀从`Stable`改为`Alt`。
+
+```py
+# 从 diffusers.pipelines.stable_diffusion.pipeline_output.StableDiffusionPipelineOutput 复制并将 Stable 替换为 Alt
+class AltDiffusionPipelineOutput(BaseOutput):
+ """
+ Output class for Alt Diffusion pipelines.
+
+ Args:
+ images (`List[PIL.Image.Image]` or `np.ndarray`)
+ List of denoised PIL images of length `batch_size` or NumPy array of shape `(batch_size, height, width,
+ num_channels)`.
+ nsfw_content_detected (`List[bool]`)
+ List indicating whether the corresponding generated image contains "not-safe-for-work" (nsfw) content or
+ `None` if safety checking could not be performed.
+ """
+```
+
+要了解更多信息,请阅读[~不要~重复自己*](https://huggingface.co/blog/transformers-design-philosophy#4-machine-learning-models-are-static)博客文章的相应部分。
+
+## 如何撰写优质问题
+
+**问题描述越清晰,被快速解决的可能性就越高。**
+
+1. 确保使用了正确的issue模板。您可以选择*错误报告*、*功能请求*、*API设计反馈*、*新模型/流水线/调度器添加*、*论坛*或空白issue。在[新建issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new/choose)时务必选择正确的模板。
+2. **精确描述**:为issue起一个恰当的标题。尽量用最简练的语言描述问题。提交issue时越精确,理解问题和潜在解决方案所需的时间就越少。确保一个issue只针对一个问题,不要将多个问题放在同一个issue中。如果发现多个问题,请分别创建多个issue。如果是错误报告,请尽可能精确描述错误类型——不应只写"diffusers出错"。
+3. **可复现性**:无法复现的代码片段 == 无法解决问题。如果遇到错误,维护人员必须能够**复现**它。确保包含一个可以复制粘贴到Python解释器中复现问题的代码片段。确保您的代码片段是可运行的,即没有缺少导入或图像链接等问题。issue应包含错误信息和可直接复制粘贴以复现相同错误的代码片段。如果issue涉及本地模型权重或无法被读者访问的本地数据,则问题无法解决。如果无法共享数据或模型,请尝试创建虚拟模型或虚拟数据。
+4. **最小化原则**:通过尽可能简洁的描述帮助读者快速理解问题。删除所有与问题无关的代码/信息。如果发现错误,请创建最简单的代码示例来演示问题,不要一发现错误就把整个工作流程都转储到issue中。例如,如果在训练模型时某个阶段出现错误或训练过程中遇到问题时,应首先尝试理解训练代码的哪部分导致了错误,并用少量代码尝试复现。建议使用模拟数据替代完整数据集进行测试。
+5. 添加引用链接。当提及特定命名、方法或模型时,请务必提供引用链接以便读者理解。若涉及具体PR或issue,请确保添加对应链接。不要假设读者了解你所指内容。issue中引用链接越丰富越好。
+6. 规范格式。请确保规范格式化issue内容:Python代码使用代码语法块,错误信息使用标准代码语法。详见[GitHub官方格式文档](https://docs.github.com/en/get-started/writing-on-github/getting-started-with-writing-and-formatting-on-github/basic-writing-and-formatting-syntax)。
+7. 请将issue视为百科全书的精美词条,而非待解决的工单。每个规范撰写的issue不仅是向维护者有效传递问题的方式,更是帮助社区深入理解库特性的公共知识贡献。
+
+## 优质PR编写规范
+
+1. 保持风格统一。理解现有设计模式和语法规范,确保新增代码与代码库现有结构无缝衔接。显著偏离现有设计模式或用户界面的PR将不予合并。
+2. 聚焦单一问题。每个PR应当只解决一个明确问题,避免"顺手修复其他问题"的陷阱。包含多个无关修改的PR会极大增加审查难度。
+3. 如适用,建议添加代码片段演示新增功能的使用方法。
+4. PR标题应准确概括其核心贡献。
+5. 若PR针对某个issue,请在描述中注明issue编号以建立关联(也让关注该issue的用户知晓有人正在处理);
+6. 进行中的PR请在标题添加`[WIP]`前缀。这既能避免重复劳动,也可与待合并PR明确区分;
+7. 文本表述与格式要求请参照[优质issue编写规范](#how-to-write-a-good-issue);
+8. 确保现有测试用例全部通过;
+9. 必须添加高覆盖率测试。未经充分测试的代码不予合并。
+- 若新增`@slow`测试,请使用`RUN_SLOW=1 python -m pytest tests/test_my_new_model.py`确保通过。
+CircleCI不执行慢速测试,但GitHub Actions会每日夜间运行!
+10. 所有公开方法必须包含格式规范、兼容markdown的说明文档。可参考[`pipeline_latent_diffusion.py`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/latent_diffusion/pipeline_latent_diffusion.py)
+11. 由于代码库快速增长,必须确保不会添加明显增加仓库体积的文件(如图片、视频等非文本文件)。建议优先使用托管在hf.co的`dataset`(例如[`hf-internal-testing`](https://huggingface.co/hf-internal-testing)或[huggingface/documentation-images](https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images))存放这类文件。若为外部贡献,可将图片添加到PR中并请Hugging Face成员将其迁移至该数据集。
+
+## 提交PR流程
+
+编写代码前,强烈建议先搜索现有PR或issue,确认没有重复工作。如有疑问,建议先创建issue获取反馈。
+
+贡献至🧨 Diffusers需要基本的`git`技能。虽然`git`学习曲线较高,但其拥有最完善的手册。在终端输入`git --help`即可查阅,或参考书籍[Pro Git](https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2)。
+
+请按以下步骤操作([支持的Python版本](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/83bc6c94eaeb6f7704a2a428931cf2d9ad973ae9/setup.py#L270)):
+
+1. 在[仓库页面](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers)点击"Fork"按钮创建代码副本至您的GitHub账户
+
+2. 克隆fork到本地,并添加主仓库为远程源:
+ ```bash
+ $ git clone git@github.com:<您的GitHub账号>/diffusers.git
+ $ cd diffusers
+ $ git remote add upstream https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers.git
+ ```
+
+3. 创建新分支进行开发:
+ ```bash
+ $ git checkout -b 您的开发分支名称
+ ```
+**禁止**直接在`main`分支上修改
+
+4. 在虚拟环境中运行以下命令配置开发环境:
+ ```bash
+ $ pip install -e ".[dev]"
+ ```
+若已克隆仓库,可能需要先执行`git pull`获取最新代码
+
+5. 在您的分支上开发功能
+
+开发过程中应确保测试通过。可运行受影响测试:
+ ```bash
+ $ pytest tests/<待测文件>.py
+ ```
+执行测试前请安装测试依赖:
+ ```bash
+ $ pip install -e ".[test]"
+ ```
+也可运行完整测试套件(需高性能机器):
+ ```bash
+ $ make test
+ ```
+
+🧨 Diffusers使用`black`和`isort`工具保持代码风格统一。修改后请执行自动化格式校正与代码验证,以下内容无法通过以下命令一次性自动化完成:
+
+```bash
+$ make style
+```
+
+🧨 Diffusers 还使用 `ruff` 和一些自定义脚本来检查代码错误。虽然质量控制流程会在 CI 中运行,但您也可以通过以下命令手动执行相同的检查:
+
+```bash
+$ make quality
+```
+
+当您对修改满意后,使用 `git add` 添加更改的文件,并通过 `git commit` 在本地记录这些更改:
+
+```bash
+$ git add modified_file.py
+$ git commit -m "关于您所做更改的描述性信息。"
+```
+
+定期将您的代码副本与原始仓库同步是一个好习惯。这样可以快速适应上游变更:
+
+```bash
+$ git pull upstream main
+```
+
+使用以下命令将更改推送到您的账户:
+
+```bash
+$ git push -u origin 此处替换为您的描述性分支名称
+```
+
+6. 确认无误后,请访问您 GitHub 账户中的派生仓库页面。点击「Pull request」将您的更改提交给项目维护者审核。
+
+7. 如果维护者要求修改,这很正常——核心贡献者也会遇到这种情况!为了让所有人能在 Pull request 中看到变更,请在本地分支继续工作并将修改推送到您的派生仓库,这些变更会自动出现在 Pull request 中。
+
+### 测试
+
+我们提供了全面的测试套件来验证库行为和多个示例。库测试位于 [tests 文件夹](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/tests)。
+
+我们推荐使用 `pytest` 和 `pytest-xdist`,因为它们速度更快。在仓库根目录下运行以下命令执行库测试:
+
+```bash
+$ python -m pytest -n auto --dist=loadfile -s -v ./tests/
+```
+
+实际上,这就是 `make test` 的实现方式!
+
+您可以指定更小的测试范围来仅验证您正在开发的功能。
+
+默认情况下会跳过耗时测试。设置 `RUN_SLOW` 环境变量为 `yes` 可运行这些测试。注意:这将下载数十 GB 的模型文件——请确保您有足够的磁盘空间、良好的网络连接或充足的耐心!
+
+```bash
+$ RUN_SLOW=yes python -m pytest -n auto --dist=loadfile -s -v ./tests/
+```
+
+我们也完全支持 `unittest`,运行方式如下:
+
+```bash
+$ python -m unittest discover -s tests -t . -v
+$ python -m unittest discover -s examples -t examples -v
+```
+
+### 将派生仓库的 main 分支与上游(HuggingFace)main 分支同步
+
+为避免向上游仓库发送引用通知(这会给相关 PR 添加注释并向开发者发送不必要的通知),在同步派生仓库的 main 分支时,请遵循以下步骤:
+1. 尽可能避免通过派生仓库的分支和 PR 来同步上游,而是直接合并到派生仓库的 main 分支
+2. 如果必须使用 PR,请在检出分支后执行以下操作:
+```bash
+$ git checkout -b 您的同步分支名称
+$ git pull --squash --no-commit upstream main
+$ git commit -m '提交信息(不要包含 GitHub 引用)'
+$ git push --set-upstream origin 您的分支名称
+```
+
+### 风格指南
+
+对于文档字符串,🧨 Diffusers 遵循 [Google 风格指南](https://google.github.io/styleguide/pyguide.html)。
diff --git a/docs/source/zh/conceptual/ethical_guidelines.md b/docs/source/zh/conceptual/ethical_guidelines.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000000..535cc86e5f0c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/source/zh/conceptual/ethical_guidelines.md
@@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
+
+
+# 🧨 Diffusers伦理准则
+
+## 前言
+
+[Diffusers](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/index)不仅提供预训练的diffusion模型,还是一个模块化工具箱,支持推理和训练功能。
+
+鉴于该技术在实际场景中的应用及其可能对社会产生的负面影响,我们认为有必要制定项目伦理准则,以指导Diffusers库的开发、用户贡献和使用规范。
+
+该技术涉及的风险仍在持续评估中,主要包括但不限于:艺术家版权问题、深度伪造滥用、不当情境下的色情内容生成、非自愿的人物模仿、以及加剧边缘群体压迫的有害社会偏见。我们将持续追踪风险,并根据社区反馈动态调整本准则。
+
+## 适用范围
+
+Diffusers社区将在项目开发中贯彻以下伦理准则,并协调社区贡献的整合方式,特别是在涉及伦理敏感议题的技术决策时。
+
+## 伦理准则
+
+以下准则具有普遍适用性,但我们主要在处理涉及伦理敏感问题的技术决策时实施。同时,我们承诺将根据技术发展带来的新兴风险持续调整这些原则:
+
+- **透明度**:我们承诺以透明方式管理PR(拉取请求),向用户解释决策依据,并公开技术选择过程。
+
+- **一致性**:我们承诺为用户提供统一标准的项目管理,保持技术稳定性和连贯性。
+
+- **简洁性**:为了让Diffusers库更易使用和开发,我们承诺保持项目目标精简且逻辑自洽。
+
+- **可及性**:本项目致力于降低贡献门槛,即使非技术人员也能参与运营,从而使研究资源更广泛地服务于社区。
+
+- **可复现性**:对于通过Diffusers库发布的上游代码、模型和数据集,我们将明确说明其可复现性。
+
+- **责任性**:作为社区和团队,我们共同承担用户责任,通过风险预判和缓解措施来应对技术潜在危害。
+
+## 实施案例:安全功能与机制
+
+团队持续开发技术和非技术工具,以应对diffusion技术相关的伦理与社会风险。社区反馈对于功能实施和风险意识提升具有不可替代的价值:
+
+- [**社区讨论区**](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/repositories-pull-requests-discussions):促进社区成员就项目开展协作讨论。
+
+- **偏见探索与评估**:Hugging Face团队提供[交互空间](https://huggingface.co/spaces/society-ethics/DiffusionBiasExplorer)展示Stable Diffusion中的偏见。我们支持并鼓励此类偏见探索与评估工作。
+
+- **部署安全强化**:
+
+ - [**Safe Stable Diffusion**](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/stable_diffusion_safe):解决Stable Diffusion等基于未过滤网络爬取数据训练的模型容易产生不当内容的问题。相关论文:[Safe Latent Diffusion:缓解diffusion模型中的不当退化](https://huggingface.co/papers/2211.05105)。
+
+ - [**安全检测器**](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/stable_diffusion/safety_checker.py):通过比对图像生成后嵌入空间中硬编码有害概念集的类别概率进行检测。有害概念列表经特殊处理以防逆向工程。
+
+- **分阶段模型发布**:对于高度敏感的仓库,采用分级访问控制。这种阶段性发布机制让作者能更好地管控使用场景。
+
+- **许可证制度**:采用新型[OpenRAILs](https://huggingface.co/blog/open_rail)许可协议,在保障开放访问的同时设置使用限制以确保更负责任的应用。
diff --git a/docs/source/zh/conceptual/evaluation.md b/docs/source/zh/conceptual/evaluation.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000000..e809c8730d34
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/source/zh/conceptual/evaluation.md
@@ -0,0 +1,558 @@
+
+
+# Diffusion模型评估指南
+
+
+
+
+无论您选择以何种方式贡献,我们都致力于成为一个开放、友好、善良的社区。请阅读我们的[行为准则](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md),并在互动时注意遵守。我们也建议您了解指导本项目的[伦理准则](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/conceptual/ethical_guidelines),并请您遵循同样的透明度和责任原则。
+
+我们高度重视社区的反馈,所以如果您认为自己有能帮助改进库的有价值反馈,请不要犹豫说出来——每条消息、评论、issue和拉取请求(PR)都会被阅读和考虑。
+
+## 概述
+
+您可以通过多种方式做出贡献,从在issue和讨论区回答问题,到向核心库添加新的diffusion模型。
+
+下面我们按难度升序列出不同的贡献方式,所有方式对社区都很有价值:
+
+* 1. 在[Diffusers讨论论坛](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers)或[Discord](https://discord.gg/G7tWnz98XR)上提问和回答问题
+* 2. 在[GitHub Issues标签页](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new/choose)提交新issue,或在[GitHub Discussions标签页](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/discussions/new/choose)发起新讨论
+* 3. 在[GitHub Issues标签页](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues)解答issue,或在[GitHub Discussions标签页](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/discussions)参与讨论
+* 4. 解决标记为"Good first issue"的简单问题,详见[此处](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22good+first+issue%22)
+* 5. 参与[文档](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/docs/source)建设
+* 6. 贡献[社区Pipeline](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3Acommunity-examples)
+* 7. 完善[示例代码](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples)
+* 8. 解决标记为"Good second issue"的中等难度问题,详见[此处](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22Good+second+issue%22)
+* 9. 添加新pipeline/模型/调度器,参见["New Pipeline/Model"](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22New+pipeline%2Fmodel%22)和["New scheduler"](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22New+scheduler%22)类issue。此类贡献请先阅读[设计哲学](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/PHILOSOPHY.md)
+
+重申:**所有贡献对社区都具有重要价值。**下文将详细说明各类贡献方式。
+
+对于4-9类贡献,您需要提交PR(拉取请求),具体操作详见[如何提交PR](#how-to-open-a-pr)章节。
+
+### 1. 在Diffusers讨论区或Discord提问与解答
+
+任何与Diffusers库相关的问题或讨论都可以发布在[官方论坛](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers/)或[Discord频道](https://discord.gg/G7tWnz98XR),包括但不限于:
+- 分享训练/推理实验报告
+- 展示个人项目
+- 咨询非官方训练示例
+- 项目提案
+- 通用反馈
+- 论文解读
+- 基于Diffusers库的个人项目求助
+- 一般性问题
+- 关于diffusion模型的伦理讨论
+- ...
+
+论坛/Discord上的每个问题都能促使社区公开分享知识,很可能帮助未来遇到相同问题的初学者。请务必提出您的疑问。
+同样地,通过回答问题您也在为社区创造公共知识文档,这种贡献极具价值。
+
+**请注意**:提问/回答时投入的精力越多,产生的公共知识质量就越高。精心构建的问题与专业解答能形成高质量知识库,而表述不清的问题则可能降低讨论价值。
+
+低质量的问题或回答会降低公共知识库的整体质量。
+简而言之,高质量的问题或回答应具备*精确性*、*简洁性*、*相关性*、*易于理解*、*可访问性*和*格式规范/表述清晰*等特质。更多详情请参阅[如何提交优质议题](#how-to-write-a-good-issue)章节。
+
+**关于渠道的说明**:
+[*论坛*](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers/63)的内容能被谷歌等搜索引擎更好地收录,且帖子按热度而非时间排序,便于查找历史问答。此外,论坛内容更容易被直接链接引用。
+而*Discord*采用即时聊天模式,适合快速交流。虽然在Discord上可能更快获得解答,但信息会随时间淹没,且难以回溯历史讨论。因此我们强烈建议在论坛发布优质问答,以构建可持续的社区知识库。若Discord讨论产生有价值结论,建议将成果整理发布至论坛以惠及更多读者。
+
+### 2. 在GitHub议题页提交新议题
+
+🧨 Diffusers库的稳健性离不开用户的问题反馈,感谢您的报错。
+
+请注意:GitHub议题仅限处理与Diffusers库代码直接相关的技术问题、错误报告、功能请求或库设计反馈。
+简言之,**与Diffusers库代码(含文档)无关**的内容应发布至[论坛](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers/63)或[Discord](https://discord.gg/G7tWnz98XR)。
+
+**提交新议题时请遵循以下准则**:
+- 确认是否已有类似议题(使用GitHub议题页的搜索栏)
+- 请勿在现有议题下追加新问题。若存在高度关联议题,应新建议题并添加相关链接
+- 确保使用英文提交。非英语用户可通过[DeepL](https://www.deepl.com/translator)等免费工具翻译
+- 检查升级至最新Diffusers版本是否能解决问题。提交前请确认`python -c "import diffusers; print(diffusers.__version__)"`显示的版本号不低于最新版本
+- 记请记住,你在提交新issue时投入的精力越多,得到的回答质量就越高,Diffusers项目的整体issue质量也会越好。
+
+新issue通常包含以下内容:
+
+#### 2.1 可复现的最小化错误报告
+
+错误报告应始终包含可复现的代码片段,并尽可能简洁明了。具体而言:
+- 尽量缩小问题范围,**不要直接粘贴整个代码文件**
+- 规范代码格式
+- 除Diffusers依赖库外,不要包含其他外部库
+- **务必**提供环境信息:可在终端运行`diffusers-cli env`命令,然后将显示的信息复制到issue中
+- 详细说明问题。如果读者不清楚问题所在及其影响,就无法解决问题
+- **确保**读者能以最小成本复现问题。如果代码片段因缺少库或未定义变量而无法运行,读者将无法提供帮助。请确保提供的可复现代码尽可能精简,可直接复制到Python shell运行
+- 如需特定模型/数据集复现问题,请确保读者能获取这些资源。可将模型/数据集上传至[Hub](https://huggingface.co)便于下载。尽量保持模型和数据集体积最小化,降低复现难度
+
+更多信息请参阅[如何撰写优质issue](#how-to-write-a-good-issue)章节。
+
+提交错误报告请点击[此处](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=bug&projects=&template=bug-report.yml)。
+
+#### 2.2 功能请求
+
+优质的功能请求应包含以下要素:
+
+1. 首先说明动机:
+* 是否与库的使用痛点相关?若是,请解释原因,最好提供演示问题的代码片段
+* 是否因项目需求产生?我们很乐意了解详情!
+* 是否是你已实现且认为对社区有价值的功能?请说明它为你解决了什么问题
+2. 用**完整段落**描述功能特性
+3. 提供**代码片段**演示预期用法
+4. 如涉及论文,请附上链接
+5. 可补充任何有助于理解的辅助材料(示意图、截图等)
+
+提交功能请求请点击[此处](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=&template=feature_request.md&title=)。
+
+#### 2.3 设计反馈
+
+关于库设计的反馈(无论正面还是负面)能极大帮助核心维护者打造更友好的库。要了解当前设计理念,请参阅[此文档](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/conceptual/philosophy)如果您认为某个设计选择与当前理念不符,请说明原因及改进建议。如果某个设计选择因过度遵循理念而限制了使用场景,也请解释原因并提出调整方案。
+若某个设计对您特别实用,请同样留下备注——这对未来的设计决策极具参考价值。
+
+您可通过[此链接](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=&template=feedback.md&title=)提交设计反馈。
+
+#### 2.4 技术问题
+
+技术问题主要涉及库代码的实现逻辑或特定功能模块的作用。提问时请务必:
+- 附上相关代码链接
+- 详细说明难以理解的具体原因
+
+技术问题提交入口:[点击此处](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=bug&template=bug-report.yml)
+
+#### 2.5 新模型/调度器/pipeline提案
+
+若diffusion模型社区发布了您希望集成到Diffusers库的新模型、pipeline或调度器,请提供以下信息:
+* 简要说明并附论文或发布链接
+* 开源实现链接(如有)
+* 模型权重下载链接(如已公开)
+
+若您愿意参与开发,请告知我们以便指导。另请尝试通过GitHub账号标记原始组件作者。
+
+提案提交地址:[新建请求](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=New+model%2Fpipeline%2Fscheduler&template=new-model-addition.yml)
+
+### 3. 解答GitHub问题
+
+回答GitHub问题可能需要Diffusers的技术知识,但我们鼓励所有人尝试参与——即使您对答案不完全正确。高质量回答的建议:
+- 保持简洁精炼
+- 严格聚焦问题本身
+- 提供代码/论文等佐证材料
+- 优先用代码说话:若代码片段能解决问题,请提供完整可复现代码
+
+许多问题可能存在离题、重复或无关情况。您可以通过以下方式协助维护者:
+- 引导提问者精确描述问题
+- 标记重复issue并附原链接
+- 推荐用户至[论坛](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers/63)或[Discord](https://discord.gg/G7tWnz98XR)
+
+在确认提交的Bug报告正确且需要修改源代码后,请继续阅读以下章节内容。
+
+以下所有贡献都需要提交PR(拉取请求)。具体操作步骤详见[如何提交PR](#how-to-open-a-pr)章节。
+
+### 4. 修复"Good first issue"类问题
+
+标有[Good first issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22good+first+issue%22)标签的问题通常已说明解决方案建议,便于修复。若该问题尚未关闭且您想尝试解决,只需留言"我想尝试解决这个问题"。通常有三种情况:
+- a.) 问题描述已提出解决方案。若您认可该方案,可直接提交PR或草稿PR进行修复
+- b.) 问题描述未提出解决方案。您可询问修复建议,Diffusers团队会尽快回复。若有成熟解决方案,也可直接提交PR
+- c.) 已有PR但问题未关闭。若原PR停滞,可新开PR并关联原PR(开源社区常见现象)。若PR仍活跃,您可通过建议、审查或协作等方式帮助原作者
+
+### 5. 文档贡献
+
+优秀库**必然**拥有优秀文档!官方文档是新用户的首要接触点,因此文档贡献具有**极高价值**。贡献形式包括:
+- 修正拼写/语法错误
+- 修复文档字符串格式错误(如显示异常或链接失效)
+- 修正文档字符串中张量的形状/维度描述
+- 优化晦涩或错误的说明
+- 更新过时代码示例
+- 文档翻译
+
+[官方文档页面](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/index)所有内容均属可修改范围,对应[文档源文件](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/docs/source)可进行编辑。修改前请查阅[验证说明](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/docs)。
+
+### 6. 贡献社区流程
+
+> [!TIP]
+> 阅读[社区流程](../using-diffusers/custom_pipeline_overview#community-pipelines)指南了解GitHub与Hugging Face Hub社区流程的区别。若想了解我们设立社区流程的原因,请查看GitHub Issue [#841](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/841)(简而言之,我们无法维护diffusion模型所有可能的推理使用方式,但也不希望限制社区构建这些流程)。
+
+贡献社区流程是向社区分享创意与成果的绝佳方式。您可以在[`DiffusionPipeline`]基础上构建流程,任何人都能通过设置`custom_pipeline`参数加载使用。本节将指导您创建一个简单的"单步"流程——UNet仅执行单次前向传播并调用调度器一次。
+
+1. 为社区流程创建one_step_unet.py文件。只要用户已安装相关包,该文件可包含任意所需包。确保仅有一个继承自[`DiffusionPipeline`]的流程类,用于从Hub加载模型权重和调度器配置。在`__init__`函数中添加UNet和调度器。
+
+ 同时添加`register_modules`函数,确保您的流程及其组件可通过[`~DiffusionPipeline.save_pretrained`]保存。
+
+```py
+from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
+import torch
+
+class UnetSchedulerOneForwardPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
+ def __init__(self, unet, scheduler):
+ super().__init__()
+
+ self.register_modules(unet=unet, scheduler=scheduler)
+```
+
+2. 在前向传播中(建议定义为`__call__`),可添加任意功能。对于"单步"流程,创建随机图像并通过设置`timestep=1`调用UNet和调度器一次。
+
+```py
+ from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
+ import torch
+
+ class UnetSchedulerOneForwardPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
+ def __init__(self, unet, scheduler):
+ super().__init__()
+
+ self.register_modules(unet=unet, scheduler=scheduler)
+
+ def __call__(self):
+ image = torch.randn(
+ (1, self.unet.config.in_channels, self.unet.config.sample_size, self.unet.config.sample_size),
+ )
+ timestep = 1
+
+ model_output = self.unet(image, timestep).sample
+ scheduler_output = self.scheduler.step(model_output, timestep, image).prev_sample
+
+ return scheduler_output
+```
+
+现在您可以通过传入UNet和调度器来运行流程,若流程结构相同也可加载预训练权重。
+
+```python
+from diffusers import DDPMScheduler, UNet2DModel
+
+scheduler = DDPMScheduler()
+unet = UNet2DModel()
+
+pipeline = UnetSchedulerOneForwardPipeline(unet=unet, scheduler=scheduler)
+output = pipeline()
+# 加载预训练权重
+pipeline = UnetSchedulerOneForwardPipeline.from_pretrained("google/ddpm-cifar10-32", use_safetensors=True)
+output = pipeline()
+```
+
+您可以选择将pipeline作为GitHub社区pipeline或Hub社区pipeline进行分享。
+
+
+
+
+通过向Diffusers[代码库](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers)提交拉取请求来分享GitHub pipeline,将one_step_unet.py文件添加到[examples/community](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/community)子文件夹中。
+
+
+
+
+通过在Hub上创建模型仓库并上传one_step_unet.py文件来分享Hub pipeline。
+
+
+
+
+### 7. 贡献训练示例
+
+Diffusers训练示例是位于[examples](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples)目录下的训练脚本集合。
+
+我们支持两种类型的训练示例:
+
+- 官方训练示例
+- 研究型训练示例
+
+研究型训练示例位于[examples/research_projects](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/research_projects),而官方训练示例包含[examples](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples)目录下除`research_projects`和`community`外的所有文件夹。
+官方训练示例由Diffusers核心维护者维护,研究型训练示例则由社区维护。
+这与[6. 贡献社区pipeline](#6-contribute-a-community-pipeline)中关于官方pipeline与社区pipeline的原因相同:核心维护者不可能维护diffusion模型的所有可能训练方法。
+如果Diffusers核心维护者和社区认为某种训练范式过于实验性或不够普及,相应训练代码应放入`research_projects`文件夹并由作者维护。
+
+官方训练和研究型示例都包含一个目录,其中含有一个或多个训练脚本、`requirements.txt`文件和`README.md`文件。用户使用时需要先克隆代码库:
+
+```bash
+git clone https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers
+```
+
+并安装训练所需的所有额外依赖:
+
+```bash
+cd diffusers
+pip install -r examples//requirements.txt
+```
+
+因此添加示例时,`requirements.txt`文件应定义训练示例所需的所有pip依赖项,安装完成后用户即可运行示例训练脚本。可参考[DreamBooth的requirements.txt文件](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/examples/dreambooth/requirements.txt)。
+- 运行示例所需的所有代码应集中在单个Python文件中
+- 用户应能通过命令行`python .py --args`直接运行示例
+- **示例**应保持简洁,主要展示如何使用Diffusers进行训练。示例脚本的目的**不是**创建最先进的diffusion模型,而是复现已知训练方案,避免添加过多自定义逻辑。因此,这些示例也力求成为优质的教学材料。
+
+提交示例时,强烈建议参考现有示例(如[dreambooth](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/examples/dreambooth/train_dreambooth.py))来了解规范格式。
+我们强烈建议贡献者使用[Accelerate库](https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate),因其与Diffusers深度集成。
+当示例脚本完成后,请确保添加详细的`README.md`说明使用方法,包括:
+- 运行示例的具体命令(示例参见[此处](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/dreambooth#running-locally-with-pytorch))
+- 训练结果链接(日志/模型等),展示用户可预期的效果(示例参见[此处](https://api.wandb.ai/report/patrickvonplaten/xm6cd5q5))
+- 若添加非官方/研究性训练示例,**必须注明**维护者信息(含Git账号),格式参照[此处](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/research_projects/intel_opts#diffusers-examples-with-intel-optimizations)
+
+贡献官方训练示例时,还需在对应目录添加测试文件(如[examples/dreambooth/test_dreambooth.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/examples/dreambooth/test_dreambooth.py)),非官方示例无需此步骤。
+
+### 8. 处理"Good second issue"类问题
+
+标有[Good second issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22Good+second+issue%22)标签的问题通常比[Good first issues](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22good+first+issue%22)更复杂。
+这类问题的描述通常不会提供详细解决指引,需要贡献者对库有较深理解。
+若您想解决此类问题,可直接提交PR并关联对应issue。若已有未合并的PR,请分析原因后提交改进版。需注意,Good second issue类PR的合并难度通常高于good first issues。在需要帮助的时候请不要犹豫,大胆的向核心维护者询问。
+
+### 9. 添加管道、模型和调度器
+
+管道(pipelines)、模型(models)和调度器(schedulers)是Diffusers库中最重要的组成部分。它们提供了对最先进diffusion技术的便捷访问,使得社区能够构建强大的生成式AI应用。
+
+通过添加新的模型、管道或调度器,您可能为依赖Diffusers的任何用户界面开启全新的强大用例,这对整个生成式AI生态系统具有巨大价值。
+
+Diffusers针对这三类组件都有一些开放的功能请求——如果您还不确定要添加哪个具体组件,可以浏览以下链接:
+- [模型或管道](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22New+pipeline%2Fmodel%22)
+- [调度器](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22New+scheduler%22)
+
+在添加任何组件之前,强烈建议您阅读[设计哲学指南](philosophy),以更好地理解这三类组件的设计理念。请注意,如果添加的模型、调度器或管道与我们的设计理念存在严重分歧,我们将无法合并,因为这会导致API不一致。如果您从根本上不同意某个设计选择,请改为提交[反馈问题](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=&template=feedback.md&title=),以便讨论是否应该更改库中的特定设计模式/选择,以及是否更新我们的设计哲学。保持库内的一致性对我们非常重要。
+
+请确保在PR中添加原始代码库/论文的链接,并最好直接在PR中@原始作者,以便他们可以跟踪进展并在有疑问时提供帮助。
+
+如果您在PR过程中遇到不确定或卡住的情况,请随时留言请求初步审查或帮助。
+
+#### 复制机制(Copied from)
+
+在添加任何管道、模型或调度器代码时,理解`# Copied from`机制是独特且重要的。您会在整个Diffusers代码库中看到这种机制,我们使用它的原因是为了保持代码库易于理解和维护。用`# Copied from`机制标记代码会强制标记的代码与复制来源的代码完全相同。这使得每当您运行`make fix-copies`时,可以轻松更新并将更改传播到多个文件。
+
+例如,在下面的代码示例中,[`~diffusers.pipelines.stable_diffusion.StableDiffusionPipelineOutput`]是原始代码,而`AltDiffusionPipelineOutput`使用`# Copied from`机制来复制它。唯一的区别是将类前缀从`Stable`改为`Alt`。
+
+```py
+# 从 diffusers.pipelines.stable_diffusion.pipeline_output.StableDiffusionPipelineOutput 复制并将 Stable 替换为 Alt
+class AltDiffusionPipelineOutput(BaseOutput):
+ """
+ Output class for Alt Diffusion pipelines.
+
+ Args:
+ images (`List[PIL.Image.Image]` or `np.ndarray`)
+ List of denoised PIL images of length `batch_size` or NumPy array of shape `(batch_size, height, width,
+ num_channels)`.
+ nsfw_content_detected (`List[bool]`)
+ List indicating whether the corresponding generated image contains "not-safe-for-work" (nsfw) content or
+ `None` if safety checking could not be performed.
+ """
+```
+
+要了解更多信息,请阅读[~不要~重复自己*](https://huggingface.co/blog/transformers-design-philosophy#4-machine-learning-models-are-static)博客文章的相应部分。
+
+## 如何撰写优质问题
+
+**问题描述越清晰,被快速解决的可能性就越高。**
+
+1. 确保使用了正确的issue模板。您可以选择*错误报告*、*功能请求*、*API设计反馈*、*新模型/流水线/调度器添加*、*论坛*或空白issue。在[新建issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new/choose)时务必选择正确的模板。
+2. **精确描述**:为issue起一个恰当的标题。尽量用最简练的语言描述问题。提交issue时越精确,理解问题和潜在解决方案所需的时间就越少。确保一个issue只针对一个问题,不要将多个问题放在同一个issue中。如果发现多个问题,请分别创建多个issue。如果是错误报告,请尽可能精确描述错误类型——不应只写"diffusers出错"。
+3. **可复现性**:无法复现的代码片段 == 无法解决问题。如果遇到错误,维护人员必须能够**复现**它。确保包含一个可以复制粘贴到Python解释器中复现问题的代码片段。确保您的代码片段是可运行的,即没有缺少导入或图像链接等问题。issue应包含错误信息和可直接复制粘贴以复现相同错误的代码片段。如果issue涉及本地模型权重或无法被读者访问的本地数据,则问题无法解决。如果无法共享数据或模型,请尝试创建虚拟模型或虚拟数据。
+4. **最小化原则**:通过尽可能简洁的描述帮助读者快速理解问题。删除所有与问题无关的代码/信息。如果发现错误,请创建最简单的代码示例来演示问题,不要一发现错误就把整个工作流程都转储到issue中。例如,如果在训练模型时某个阶段出现错误或训练过程中遇到问题时,应首先尝试理解训练代码的哪部分导致了错误,并用少量代码尝试复现。建议使用模拟数据替代完整数据集进行测试。
+5. 添加引用链接。当提及特定命名、方法或模型时,请务必提供引用链接以便读者理解。若涉及具体PR或issue,请确保添加对应链接。不要假设读者了解你所指内容。issue中引用链接越丰富越好。
+6. 规范格式。请确保规范格式化issue内容:Python代码使用代码语法块,错误信息使用标准代码语法。详见[GitHub官方格式文档](https://docs.github.com/en/get-started/writing-on-github/getting-started-with-writing-and-formatting-on-github/basic-writing-and-formatting-syntax)。
+7. 请将issue视为百科全书的精美词条,而非待解决的工单。每个规范撰写的issue不仅是向维护者有效传递问题的方式,更是帮助社区深入理解库特性的公共知识贡献。
+
+## 优质PR编写规范
+
+1. 保持风格统一。理解现有设计模式和语法规范,确保新增代码与代码库现有结构无缝衔接。显著偏离现有设计模式或用户界面的PR将不予合并。
+2. 聚焦单一问题。每个PR应当只解决一个明确问题,避免"顺手修复其他问题"的陷阱。包含多个无关修改的PR会极大增加审查难度。
+3. 如适用,建议添加代码片段演示新增功能的使用方法。
+4. PR标题应准确概括其核心贡献。
+5. 若PR针对某个issue,请在描述中注明issue编号以建立关联(也让关注该issue的用户知晓有人正在处理);
+6. 进行中的PR请在标题添加`[WIP]`前缀。这既能避免重复劳动,也可与待合并PR明确区分;
+7. 文本表述与格式要求请参照[优质issue编写规范](#how-to-write-a-good-issue);
+8. 确保现有测试用例全部通过;
+9. 必须添加高覆盖率测试。未经充分测试的代码不予合并。
+- 若新增`@slow`测试,请使用`RUN_SLOW=1 python -m pytest tests/test_my_new_model.py`确保通过。
+CircleCI不执行慢速测试,但GitHub Actions会每日夜间运行!
+10. 所有公开方法必须包含格式规范、兼容markdown的说明文档。可参考[`pipeline_latent_diffusion.py`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/latent_diffusion/pipeline_latent_diffusion.py)
+11. 由于代码库快速增长,必须确保不会添加明显增加仓库体积的文件(如图片、视频等非文本文件)。建议优先使用托管在hf.co的`dataset`(例如[`hf-internal-testing`](https://huggingface.co/hf-internal-testing)或[huggingface/documentation-images](https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images))存放这类文件。若为外部贡献,可将图片添加到PR中并请Hugging Face成员将其迁移至该数据集。
+
+## 提交PR流程
+
+编写代码前,强烈建议先搜索现有PR或issue,确认没有重复工作。如有疑问,建议先创建issue获取反馈。
+
+贡献至🧨 Diffusers需要基本的`git`技能。虽然`git`学习曲线较高,但其拥有最完善的手册。在终端输入`git --help`即可查阅,或参考书籍[Pro Git](https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2)。
+
+请按以下步骤操作([支持的Python版本](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/83bc6c94eaeb6f7704a2a428931cf2d9ad973ae9/setup.py#L270)):
+
+1. 在[仓库页面](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers)点击"Fork"按钮创建代码副本至您的GitHub账户
+
+2. 克隆fork到本地,并添加主仓库为远程源:
+ ```bash
+ $ git clone git@github.com:<您的GitHub账号>/diffusers.git
+ $ cd diffusers
+ $ git remote add upstream https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers.git
+ ```
+
+3. 创建新分支进行开发:
+ ```bash
+ $ git checkout -b 您的开发分支名称
+ ```
+**禁止**直接在`main`分支上修改
+
+4. 在虚拟环境中运行以下命令配置开发环境:
+ ```bash
+ $ pip install -e ".[dev]"
+ ```
+若已克隆仓库,可能需要先执行`git pull`获取最新代码
+
+5. 在您的分支上开发功能
+
+开发过程中应确保测试通过。可运行受影响测试:
+ ```bash
+ $ pytest tests/<待测文件>.py
+ ```
+执行测试前请安装测试依赖:
+ ```bash
+ $ pip install -e ".[test]"
+ ```
+也可运行完整测试套件(需高性能机器):
+ ```bash
+ $ make test
+ ```
+
+🧨 Diffusers使用`black`和`isort`工具保持代码风格统一。修改后请执行自动化格式校正与代码验证,以下内容无法通过以下命令一次性自动化完成:
+
+```bash
+$ make style
+```
+
+🧨 Diffusers 还使用 `ruff` 和一些自定义脚本来检查代码错误。虽然质量控制流程会在 CI 中运行,但您也可以通过以下命令手动执行相同的检查:
+
+```bash
+$ make quality
+```
+
+当您对修改满意后,使用 `git add` 添加更改的文件,并通过 `git commit` 在本地记录这些更改:
+
+```bash
+$ git add modified_file.py
+$ git commit -m "关于您所做更改的描述性信息。"
+```
+
+定期将您的代码副本与原始仓库同步是一个好习惯。这样可以快速适应上游变更:
+
+```bash
+$ git pull upstream main
+```
+
+使用以下命令将更改推送到您的账户:
+
+```bash
+$ git push -u origin 此处替换为您的描述性分支名称
+```
+
+6. 确认无误后,请访问您 GitHub 账户中的派生仓库页面。点击「Pull request」将您的更改提交给项目维护者审核。
+
+7. 如果维护者要求修改,这很正常——核心贡献者也会遇到这种情况!为了让所有人能在 Pull request 中看到变更,请在本地分支继续工作并将修改推送到您的派生仓库,这些变更会自动出现在 Pull request 中。
+
+### 测试
+
+我们提供了全面的测试套件来验证库行为和多个示例。库测试位于 [tests 文件夹](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/tests)。
+
+我们推荐使用 `pytest` 和 `pytest-xdist`,因为它们速度更快。在仓库根目录下运行以下命令执行库测试:
+
+```bash
+$ python -m pytest -n auto --dist=loadfile -s -v ./tests/
+```
+
+实际上,这就是 `make test` 的实现方式!
+
+您可以指定更小的测试范围来仅验证您正在开发的功能。
+
+默认情况下会跳过耗时测试。设置 `RUN_SLOW` 环境变量为 `yes` 可运行这些测试。注意:这将下载数十 GB 的模型文件——请确保您有足够的磁盘空间、良好的网络连接或充足的耐心!
+
+```bash
+$ RUN_SLOW=yes python -m pytest -n auto --dist=loadfile -s -v ./tests/
+```
+
+我们也完全支持 `unittest`,运行方式如下:
+
+```bash
+$ python -m unittest discover -s tests -t . -v
+$ python -m unittest discover -s examples -t examples -v
+```
+
+### 将派生仓库的 main 分支与上游(HuggingFace)main 分支同步
+
+为避免向上游仓库发送引用通知(这会给相关 PR 添加注释并向开发者发送不必要的通知),在同步派生仓库的 main 分支时,请遵循以下步骤:
+1. 尽可能避免通过派生仓库的分支和 PR 来同步上游,而是直接合并到派生仓库的 main 分支
+2. 如果必须使用 PR,请在检出分支后执行以下操作:
+```bash
+$ git checkout -b 您的同步分支名称
+$ git pull --squash --no-commit upstream main
+$ git commit -m '提交信息(不要包含 GitHub 引用)'
+$ git push --set-upstream origin 您的分支名称
+```
+
+### 风格指南
+
+对于文档字符串,🧨 Diffusers 遵循 [Google 风格指南](https://google.github.io/styleguide/pyguide.html)。
diff --git a/docs/source/zh/conceptual/ethical_guidelines.md b/docs/source/zh/conceptual/ethical_guidelines.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000000..535cc86e5f0c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/source/zh/conceptual/ethical_guidelines.md
@@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
+
+
+# 🧨 Diffusers伦理准则
+
+## 前言
+
+[Diffusers](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/index)不仅提供预训练的diffusion模型,还是一个模块化工具箱,支持推理和训练功能。
+
+鉴于该技术在实际场景中的应用及其可能对社会产生的负面影响,我们认为有必要制定项目伦理准则,以指导Diffusers库的开发、用户贡献和使用规范。
+
+该技术涉及的风险仍在持续评估中,主要包括但不限于:艺术家版权问题、深度伪造滥用、不当情境下的色情内容生成、非自愿的人物模仿、以及加剧边缘群体压迫的有害社会偏见。我们将持续追踪风险,并根据社区反馈动态调整本准则。
+
+## 适用范围
+
+Diffusers社区将在项目开发中贯彻以下伦理准则,并协调社区贡献的整合方式,特别是在涉及伦理敏感议题的技术决策时。
+
+## 伦理准则
+
+以下准则具有普遍适用性,但我们主要在处理涉及伦理敏感问题的技术决策时实施。同时,我们承诺将根据技术发展带来的新兴风险持续调整这些原则:
+
+- **透明度**:我们承诺以透明方式管理PR(拉取请求),向用户解释决策依据,并公开技术选择过程。
+
+- **一致性**:我们承诺为用户提供统一标准的项目管理,保持技术稳定性和连贯性。
+
+- **简洁性**:为了让Diffusers库更易使用和开发,我们承诺保持项目目标精简且逻辑自洽。
+
+- **可及性**:本项目致力于降低贡献门槛,即使非技术人员也能参与运营,从而使研究资源更广泛地服务于社区。
+
+- **可复现性**:对于通过Diffusers库发布的上游代码、模型和数据集,我们将明确说明其可复现性。
+
+- **责任性**:作为社区和团队,我们共同承担用户责任,通过风险预判和缓解措施来应对技术潜在危害。
+
+## 实施案例:安全功能与机制
+
+团队持续开发技术和非技术工具,以应对diffusion技术相关的伦理与社会风险。社区反馈对于功能实施和风险意识提升具有不可替代的价值:
+
+- [**社区讨论区**](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/repositories-pull-requests-discussions):促进社区成员就项目开展协作讨论。
+
+- **偏见探索与评估**:Hugging Face团队提供[交互空间](https://huggingface.co/spaces/society-ethics/DiffusionBiasExplorer)展示Stable Diffusion中的偏见。我们支持并鼓励此类偏见探索与评估工作。
+
+- **部署安全强化**:
+
+ - [**Safe Stable Diffusion**](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/stable_diffusion_safe):解决Stable Diffusion等基于未过滤网络爬取数据训练的模型容易产生不当内容的问题。相关论文:[Safe Latent Diffusion:缓解diffusion模型中的不当退化](https://huggingface.co/papers/2211.05105)。
+
+ - [**安全检测器**](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/stable_diffusion/safety_checker.py):通过比对图像生成后嵌入空间中硬编码有害概念集的类别概率进行检测。有害概念列表经特殊处理以防逆向工程。
+
+- **分阶段模型发布**:对于高度敏感的仓库,采用分级访问控制。这种阶段性发布机制让作者能更好地管控使用场景。
+
+- **许可证制度**:采用新型[OpenRAILs](https://huggingface.co/blog/open_rail)许可协议,在保障开放访问的同时设置使用限制以确保更负责任的应用。
diff --git a/docs/source/zh/conceptual/evaluation.md b/docs/source/zh/conceptual/evaluation.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000000..e809c8730d34
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/source/zh/conceptual/evaluation.md
@@ -0,0 +1,558 @@
+
+
+# Diffusion模型评估指南
+
+
+  +
+
+> [!TIP]
+> 鉴于当前已出现针对图像生成Diffusion模型的成熟评估框架(如[HEIM](https://crfm.stanford.edu/helm/heim/latest/)、[T2I-Compbench](https://huggingface.co/papers/2307.06350)、[GenEval](https://huggingface.co/papers/2310.11513)),本文档部分内容已过时。
+
+像 [Stable Diffusion](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/stable_diffusion) 这类生成模型的评估本质上是主观的。但作为开发者和研究者,我们经常需要在众多可能性中做出审慎选择。那么当面对不同生成模型(如 GANs、Diffusion 等)时,该如何决策?
+
+定性评估容易产生偏差,可能导致错误结论;而定量指标又未必能准确反映图像质量。因此,通常需要结合定性与定量评估来获得更可靠的模型选择依据。
+
+本文档将系统介绍扩散模型的定性与定量评估方法(非穷尽列举)。对于定量方法,我们将重点演示如何结合 `diffusers` 库实现这些评估。
+
+文档所示方法同样适用于评估不同[噪声调度器](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/schedulers/overview)在固定生成模型下的表现差异。
+
+## 评估场景
+
+我们涵盖以下Diffusion模型管线的评估:
+
+- 文本引导图像生成(如 [`StableDiffusionPipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/text2img))
+- 基于文本和输入图像的引导生成(如 [`StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/img2img) 和 [`StableDiffusionInstructPix2PixPipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/pix2pix))
+- 类别条件图像生成模型(如 [`DiTPipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipe))
+
+## 定性评估
+
+定性评估通常涉及对生成图像的人工评判。评估维度包括构图质量、图文对齐度和空间关系等方面。标准化的提示词能为这些主观指标提供统一基准。DrawBench和PartiPrompts是常用的定性评估提示词数据集,分别由[Imagen](https://imagen.research.google/)和[Parti](https://parti.research.google/)团队提出。
+
+根据[Parti官方网站](https://parti.research.google/)说明:
+
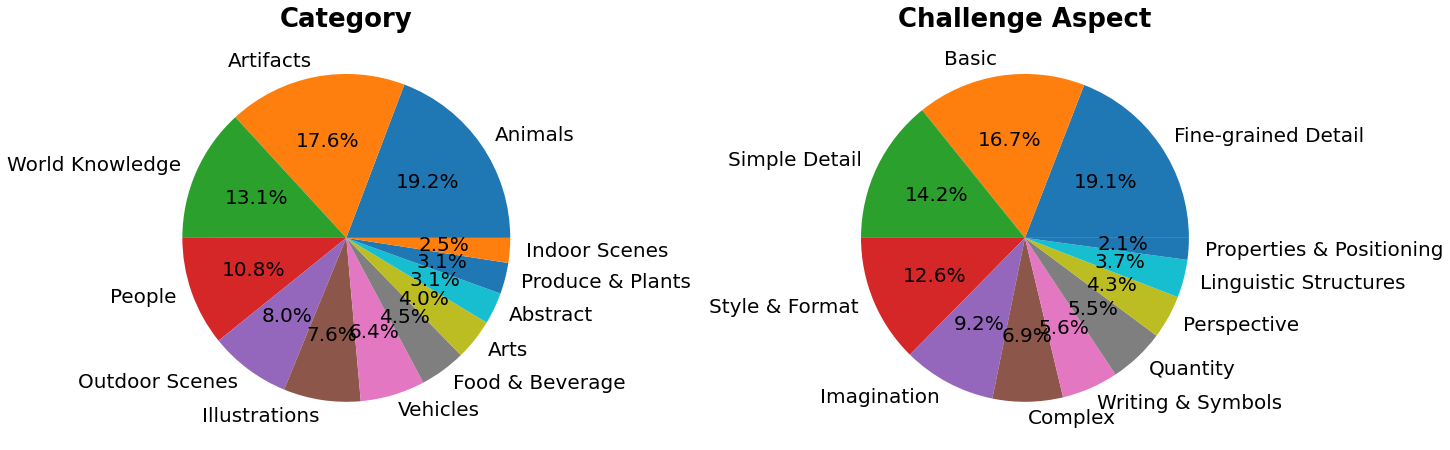
+> PartiPrompts (P2)是我们发布的包含1600多个英文提示词的丰富集合,可用于测量模型在不同类别和挑战维度上的能力。
+
+
+
+PartiPrompts包含以下字段:
+- Prompt(提示词)
+- Category(类别,如"抽象"、"世界知识"等)
+- Challenge(难度等级,如"基础"、"复杂"、"文字与符号"等)
+
+这些基准测试支持对不同图像生成模型进行并排人工对比评估。为此,🧨 Diffusers团队构建了**Open Parti Prompts**——一个基于Parti Prompts的社区驱动型定性评估基准,用于比较顶尖开源diffusion模型:
+- [Open Parti Prompts游戏](https://huggingface.co/spaces/OpenGenAI/open-parti-prompts):展示10个parti提示词对应的4张生成图像,用户选择最符合提示的图片
+- [Open Parti Prompts排行榜](https://huggingface.co/spaces/OpenGenAI/parti-prompts-leaderboard):对比当前最优开源diffusion模型的性能榜单
+
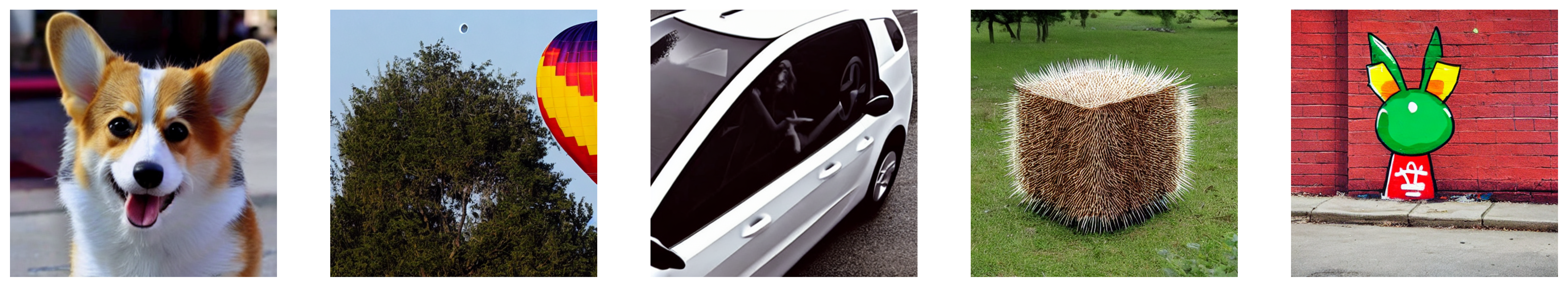
+为进行手动图像对比,我们演示如何使用`diffusers`处理部分PartiPrompts提示词。
+
+以下是从不同挑战维度(基础、复杂、语言结构、想象力、文字与符号)采样的提示词示例(使用[PartiPrompts作为数据集](https://huggingface.co/datasets/nateraw/parti-prompts)):
+
+```python
+from datasets import load_dataset
+
+# prompts = load_dataset("nateraw/parti-prompts", split="train")
+# prompts = prompts.shuffle()
+# sample_prompts = [prompts[i]["Prompt"] for i in range(5)]
+
+# Fixing these sample prompts in the interest of reproducibility.
+sample_prompts = [
+ "a corgi",
+ "a hot air balloon with a yin-yang symbol, with the moon visible in the daytime sky",
+ "a car with no windows",
+ "a cube made of porcupine",
+ 'The saying "BE EXCELLENT TO EACH OTHER" written on a red brick wall with a graffiti image of a green alien wearing a tuxedo. A yellow fire hydrant is on a sidewalk in the foreground.',
+]
+```
+
+现在我们可以使用Stable Diffusion([v1-4 checkpoint](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4))生成这些提示词对应的图像:
+
+```python
+import torch
+
+seed = 0
+generator = torch.manual_seed(seed)
+
+images = sd_pipeline(sample_prompts, num_images_per_prompt=1, generator=generator).images
+```
+
+
+
+我们也可以通过设置`num_images_per_prompt`参数来比较同一提示词生成的不同图像。使用不同检查点([v1-5](https://huggingface.co/stable-diffusion-v1-5/stable-diffusion-v1-5))运行相同流程后,结果如下:
+
+
+
+当使用多个待评估模型为所有提示词生成若干图像后,这些结果将提交给人类评估员进行打分。有关DrawBench和PartiPrompts基准测试的更多细节,请参阅各自的论文。
+
+
+
+在模型训练过程中查看推理样本有助于评估训练进度。我们的[训练脚本](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/)支持此功能,并额外提供TensorBoard和Weights & Biases日志记录功能。
+
+
+
+## 定量评估
+
+本节将指导您如何评估三种不同的扩散流程,使用以下指标:
+- CLIP分数
+- CLIP方向相似度
+- FID(弗雷歇起始距离)
+
+### 文本引导图像生成
+
+[CLIP分数](https://huggingface.co/papers/2104.08718)用于衡量图像-标题对的匹配程度。CLIP分数越高表明匹配度越高🔼。该分数是对"匹配度"这一定性概念的量化测量,也可以理解为图像与标题之间的语义相似度。研究发现CLIP分数与人类判断具有高度相关性。
+
+首先加载[`StableDiffusionPipeline`]:
+
+```python
+from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
+import torch
+
+model_ckpt = "CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4"
+sd_pipeline = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_ckpt, torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
+```
+
+使用多个提示词生成图像:
+
+```python
+prompts = [
+ "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars",
+ "A high tech solarpunk utopia in the Amazon rainforest",
+ "A pikachu fine dining with a view to the Eiffel Tower",
+ "A mecha robot in a favela in expressionist style",
+ "an insect robot preparing a delicious meal",
+ "A small cabin on top of a snowy mountain in the style of Disney, artstation",
+]
+
+images = sd_pipeline(prompts, num_images_per_prompt=1, output_type="np").images
+
+print(images.shape)
+# (6, 512, 512, 3)
+```
+
+然后计算CLIP分数:
+
+```python
+from torchmetrics.functional.multimodal import clip_score
+from functools import partial
+
+clip_score_fn = partial(clip_score, model_name_or_path="openai/clip-vit-base-patch16")
+
+def calculate_clip_score(images, prompts):
+ images_int = (images * 255).astype("uint8")
+ clip_score = clip_score_fn(torch.from_numpy(images_int).permute(0, 3, 1, 2), prompts).detach()
+ return round(float(clip_score), 4)
+
+sd_clip_score = calculate_clip_score(images, prompts)
+print(f"CLIP分数: {sd_clip_score}")
+# CLIP分数: 35.7038
+```
+
+上述示例中,我们为每个提示生成一张图像。如果为每个提示生成多张图像,则需要计算每个提示生成图像的平均分数。
+
+当需要比较两个兼容[`StableDiffusionPipeline`]的检查点时,应在调用管道时传入生成器。首先使用[v1-4 Stable Diffusion检查点](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4)以固定种子生成图像:
+
+```python
+seed = 0
+generator = torch.manual_seed(seed)
+
+images = sd_pipeline(prompts, num_images_per_prompt=1, generator=generator, output_type="np").images
+```
+
+然后加载[v1-5检查点](https://huggingface.co/stable-diffusion-v1-5/stable-diffusion-v1-5)生成图像:
+
+```python
+model_ckpt_1_5 = "stable-diffusion-v1-5/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
+sd_pipeline_1_5 = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_ckpt_1_5, torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
+
+images_1_5 = sd_pipeline_1_5(prompts, num_images_per_prompt=1, generator=generator, output_type="np").images
+```
+
+最后比较两者的CLIP分数:
+
+```python
+sd_clip_score_1_4 = calculate_clip_score(images, prompts)
+print(f"v-1-4版本的CLIP分数: {sd_clip_score_1_4}")
+# v-1-4版本的CLIP分数: 34.9102
+
+sd_clip_score_1_5 = calculate_clip_score(images_1_5, prompts)
+print(f"v-1-5版本的CLIP分数: {sd_clip_score_1_5}")
+# v-1-5版本的CLIP分数: 36.2137
+```
+
+结果表明[v1-5](https://huggingface.co/stable-diffusion-v1-5/stable-diffusion-v1-5)检查点性能优于前代。但需注意,我们用于计算CLIP分数的提示词数量较少。实际评估时应使用更多样化且数量更大的提示词集。
+
+
+
+该分数存在固有局限性:训练数据中的标题是从网络爬取,并提取自图片关联的`alt`等标签。这些描述未必符合人类描述图像的方式,因此我们需要人工"设计"部分提示词。
+
+
+
+### 图像条件式文本生成图像
+
+这种情况下,生成管道同时接受输入图像和文本提示作为条件。以[`StableDiffusionInstructPix2PixPipeline`]为例,该管道接收编辑指令作为输入提示,并接受待编辑的输入图像。
+
+示例图示:
+
+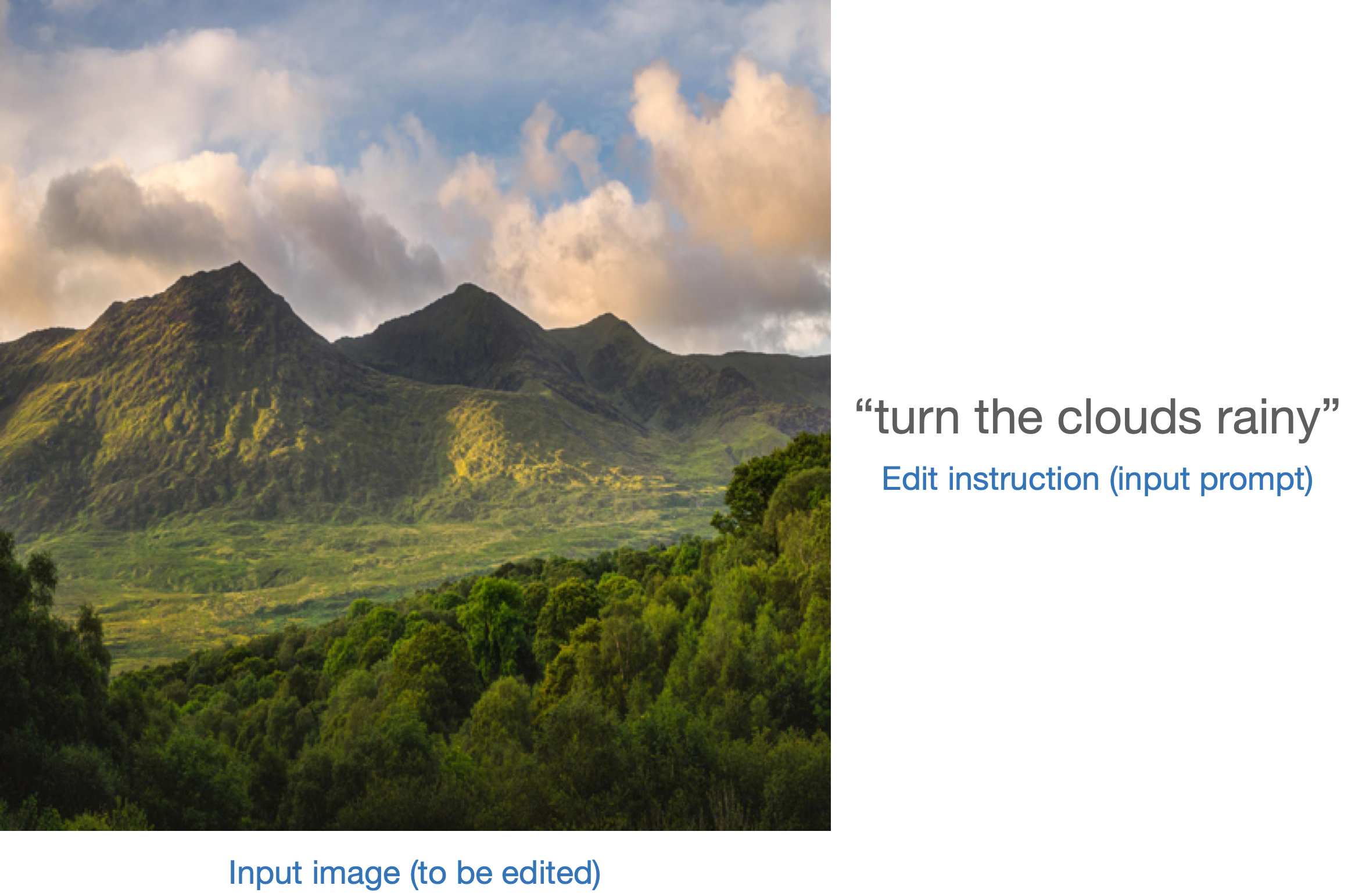
+
+评估此类模型的策略之一是测量两幅图像间变化的连贯性(通过[CLIP](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/clip)定义)中两个图像之间的变化与两个图像描述之间的变化的一致性(如论文[《CLIP-Guided Domain Adaptation of Image Generators》](https://huggingface.co/papers/2108.00946)所示)。这被称为“**CLIP方向相似度**”。
+
+- **描述1**对应输入图像(图像1),即待编辑的图像。
+- **描述2**对应编辑后的图像(图像2),应反映编辑指令。
+
+以下是示意图:
+
+
+
+我们准备了一个小型数据集来实现该指标。首先加载数据集:
+
+```python
+from datasets import load_dataset
+
+dataset = load_dataset("sayakpaul/instructpix2pix-demo", split="train")
+dataset.features
+```
+
+```bash
+{'input': Value(dtype='string', id=None),
+ 'edit': Value(dtype='string', id=None),
+ 'output': Value(dtype='string', id=None),
+ 'image': Image(decode=True, id=None)}
+```
+
+数据字段说明:
+
+- `input`:与`image`对应的原始描述。
+- `edit`:编辑指令。
+- `output`:反映`edit`指令的修改后描述。
+
+查看一个样本:
+
+```python
+idx = 0
+print(f"Original caption: {dataset[idx]['input']}")
+print(f"Edit instruction: {dataset[idx]['edit']}")
+print(f"Modified caption: {dataset[idx]['output']}")
+```
+
+```bash
+Original caption: 2. FAROE ISLANDS: An archipelago of 18 mountainous isles in the North Atlantic Ocean between Norway and Iceland, the Faroe Islands has 'everything you could hope for', according to Big 7 Travel. It boasts 'crystal clear waterfalls, rocky cliffs that seem to jut out of nowhere and velvety green hills'
+Edit instruction: make the isles all white marble
+Modified caption: 2. WHITE MARBLE ISLANDS: An archipelago of 18 mountainous white marble isles in the North Atlantic Ocean between Norway and Iceland, the White Marble Islands has 'everything you could hope for', according to Big 7 Travel. It boasts 'crystal clear waterfalls, rocky cliffs that seem to jut out of nowhere and velvety green hills'
+```
+
+对应的图像:
+
+```python
+dataset[idx]["image"]
+```
+
+
+
+我们将根据编辑指令修改数据集中的图像,并计算方向相似度。
+
+首先加载[`StableDiffusionInstructPix2PixPipeline`]:
+
+```python
+from diffusers import StableDiffusionInstructPix2PixPipeline
+
+instruct_pix2pix_pipeline = StableDiffusionInstructPix2PixPipeline.from_pretrained(
+ "timbrooks/instruct-pix2pix", torch_dtype=torch.float16
+).to("cuda")
+```
+
+执行编辑操作:
+
+```python
+import numpy as np
+
+
+def edit_image(input_image, instruction):
+ image = instruct_pix2pix_pipeline(
+ instruction,
+ image=input_image,
+ output_type="np",
+ generator=generator,
+ ).images[0]
+ return image
+
+input_images = []
+original_captions = []
+modified_captions = []
+edited_images = []
+
+for idx in range(len(dataset)):
+ input_image = dataset[idx]["image"]
+ edit_instruction = dataset[idx]["edit"]
+ edited_image = edit_image(input_image, edit_instruction)
+
+ input_images.append(np.array(input_image))
+ original_captions.append(dataset[idx]["input"])
+ modified_captions.append(dataset[idx]["output"])
+ edited_images.append(edited_image)
+```
+
+为测量方向相似度,我们首先加载CLIP的图像和文本编码器:
+
+```python
+from transformers import (
+ CLIPTokenizer,
+ CLIPTextModelWithProjection,
+ CLIPVisionModelWithProjection,
+ CLIPImageProcessor,
+)
+
+clip_id = "openai/clip-vit-large-patch14"
+tokenizer = CLIPTokenizer.from_pretrained(clip_id)
+text_encoder = CLIPTextModelWithProjection.from_pretrained(clip_id).to("cuda")
+image_processor = CLIPImageProcessor.from_pretrained(clip_id)
+image_encoder = CLIPVisionModelWithProjection.from_pretrained(clip_id).to("cuda")
+```
+
+注意我们使用的是特定CLIP检查点——`openai/clip-vit-large-patch14`,因为Stable Diffusion预训练正是基于此CLIP变体。详见[文档](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/clip)。
+
+接着准备计算方向相似度的PyTorch `nn.Module`:
+
+```python
+import torch.nn as nn
+import torch.nn.functional as F
+
+
+class DirectionalSimilarity(nn.Module):
+ def __init__(self, tokenizer, text_encoder, image_processor, image_encoder):
+ super().__init__()
+ self.tokenizer = tokenizer
+ self.text_encoder = text_encoder
+ self.image_processor = image_processor
+ self.image_encoder = image_encoder
+
+ def preprocess_image(self, image):
+ image = self.image_processor(image, return_tensors="pt")["pixel_values"]
+ return {"pixel_values": image.to("cuda")}
+
+ def tokenize_text(self, text):
+ inputs = self.tokenizer(
+ text,
+ max_length=self.tokenizer.model_max_length,
+ padding="max_length",
+ truncation=True,
+ return_tensors="pt",
+ )
+ return {"input_ids": inputs.input_ids.to("cuda")}
+
+ def encode_image(self, image):
+ preprocessed_image = self.preprocess_image(image)
+ image_features = self.image_encoder(**preprocessed_image).image_embeds
+ image_features = image_features / image_features.norm(dim=1, keepdim=True)
+ return image_features
+
+ def encode_text(self, text):
+ tokenized_text = self.tokenize_text(text)
+ text_features = self.text_encoder(**tokenized_text).text_embeds
+ text_features = text_features / text_features.norm(dim=1, keepdim=True)
+ return text_features
+
+ def compute_directional_similarity(self, img_feat_one, img_feat_two, text_feat_one, text_feat_two):
+ sim_direction = F.cosine_similarity(img_feat_two - img_feat_one, text_feat_two - text_feat_one)
+ return sim_direction
+
+ def forward(self, image_one, image_two, caption_one, caption_two):
+ img_feat_one = self.encode_image(image_one)
+ img_feat_two = self.encode_image(image_two)
+ text_feat_one = self.encode_text(caption_one)
+ text_feat_two = self.encode_text(caption_two)
+ directional_similarity = self.compute_directional_similarity(
+ img_feat_one, img_feat_two, text_feat_one, text_feat_two
+ )
+ return directional_similarity
+```
+
+现在让我们使用`DirectionalSimilarity`模块:
+
+```python
+dir_similarity = DirectionalSimilarity(tokenizer, text_encoder, image_processor, image_encoder)
+scores = []
+
+for i in range(len(input_images)):
+ original_image = input_images[i]
+ original_caption = original_captions[i]
+ edited_image = edited_images[i]
+ modified_caption = modified_captions[i]
+
+ similarity_score = dir_similarity(original_image, edited_image, original_caption, modified_caption)
+ scores.append(float(similarity_score.detach().cpu()))
+
+print(f"CLIP方向相似度: {np.mean(scores)}")
+# CLIP方向相似度: 0.0797976553440094
+```
+
+与CLIP分数类似,CLIP方向相似度数值越高越好。
+
+需要注意的是,`StableDiffusionInstructPix2PixPipeline`提供了两个控制参数`image_guidance_scale`和`guidance_scale`来调节最终编辑图像的质量。建议您尝试调整这两个参数,观察它们对方向相似度的影响。
+
+我们可以扩展这个度量标准来评估原始图像与编辑版本的相似度,只需计算`F.cosine_similarity(img_feat_two, img_feat_one)`。对于这类编辑任务,我们仍希望尽可能保留图像的主要语义特征(即保持较高的相似度分数)。
+
+该度量方法同样适用于类似流程,例如[`StableDiffusionPix2PixZeroPipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/pix2pix_zero#diffusers.StableDiffusionPix2PixZeroPipeline)。
+
+
+
+CLIP分数和CLIP方向相似度都依赖CLIP模型,可能导致评估结果存在偏差。
+
+
+
+***扩展IS、FID(后文讨论)或KID等指标存在困难***,当被评估模型是在大型图文数据集(如[LAION-5B数据集](https://laion.ai/blog/laion-5b/))上预训练时。因为这些指标的底层都使用了在ImageNet-1k数据集上预训练的InceptionNet来提取图像特征。Stable Diffusion的预训练数据集与InceptionNet的预训练数据集可能重叠有限,因此不适合作为特征提取器。
+
+***上述指标更适合评估类别条件模型***,例如[DiT](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/dit)。该模型是在ImageNet-1k类别条件下预训练的。
+这是9篇文档中的第8部分。
+
+### 基于类别的图像生成
+
+基于类别的生成模型通常是在带有类别标签的数据集(如[ImageNet-1k](https://huggingface.co/datasets/imagenet-1k))上进行预训练的。评估这些模型的常用指标包括Fréchet Inception Distance(FID)、Kernel Inception Distance(KID)和Inception Score(IS)。本文档重点介绍FID([Heusel等人](https://huggingface.co/papers/1706.08500)),并展示如何使用[`DiTPipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/pipelines/dit)计算该指标,该管道底层使用了[DiT模型](https://huggingface.co/papers/2212.09748)。
+
+FID旨在衡量两组图像数据集的相似程度。根据[此资源](https://mmgeneration.readthedocs.io/en/latest/quick_run.html#fid):
+
+> Fréchet Inception Distance是衡量两组图像数据集相似度的指标。研究表明其与人类对视觉质量的主观判断高度相关,因此最常用于评估生成对抗网络(GAN)生成样本的质量。FID通过计算Inception网络特征表示所拟合的两个高斯分布之间的Fréchet距离来实现。
+
+这两个数据集本质上是真实图像数据集和生成图像数据集(本例中为人工生成的图像)。FID通常基于两个大型数据集计算,但本文档将使用两个小型数据集进行演示。
+
+首先下载ImageNet-1k训练集中的部分图像:
+
+```python
+from zipfile import ZipFile
+import requests
+
+
+def download(url, local_filepath):
+ r = requests.get(url)
+ with open(local_filepath, "wb") as f:
+ f.write(r.content)
+ return local_filepath
+
+dummy_dataset_url = "https://hf.co/datasets/sayakpaul/sample-datasets/resolve/main/sample-imagenet-images.zip"
+local_filepath = download(dummy_dataset_url, dummy_dataset_url.split("/")[-1])
+
+with ZipFile(local_filepath, "r") as zipper:
+ zipper.extractall(".")
+```
+
+```python
+from PIL import Image
+import os
+import numpy as np
+
+dataset_path = "sample-imagenet-images"
+image_paths = sorted([os.path.join(dataset_path, x) for x in os.listdir(dataset_path)])
+
+real_images = [np.array(Image.open(path).convert("RGB")) for path in image_paths]
+```
+
+这些是来自以下ImageNet-1k类别的10张图像:"cassette_player"、"chain_saw"(2张)、"church"、"gas_pump"(3张)、"parachute"(2张)和"tench"。
+
+
+
+
+> [!TIP]
+> 鉴于当前已出现针对图像生成Diffusion模型的成熟评估框架(如[HEIM](https://crfm.stanford.edu/helm/heim/latest/)、[T2I-Compbench](https://huggingface.co/papers/2307.06350)、[GenEval](https://huggingface.co/papers/2310.11513)),本文档部分内容已过时。
+
+像 [Stable Diffusion](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/stable_diffusion) 这类生成模型的评估本质上是主观的。但作为开发者和研究者,我们经常需要在众多可能性中做出审慎选择。那么当面对不同生成模型(如 GANs、Diffusion 等)时,该如何决策?
+
+定性评估容易产生偏差,可能导致错误结论;而定量指标又未必能准确反映图像质量。因此,通常需要结合定性与定量评估来获得更可靠的模型选择依据。
+
+本文档将系统介绍扩散模型的定性与定量评估方法(非穷尽列举)。对于定量方法,我们将重点演示如何结合 `diffusers` 库实现这些评估。
+
+文档所示方法同样适用于评估不同[噪声调度器](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/schedulers/overview)在固定生成模型下的表现差异。
+
+## 评估场景
+
+我们涵盖以下Diffusion模型管线的评估:
+
+- 文本引导图像生成(如 [`StableDiffusionPipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/text2img))
+- 基于文本和输入图像的引导生成(如 [`StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/img2img) 和 [`StableDiffusionInstructPix2PixPipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/pix2pix))
+- 类别条件图像生成模型(如 [`DiTPipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipe))
+
+## 定性评估
+
+定性评估通常涉及对生成图像的人工评判。评估维度包括构图质量、图文对齐度和空间关系等方面。标准化的提示词能为这些主观指标提供统一基准。DrawBench和PartiPrompts是常用的定性评估提示词数据集,分别由[Imagen](https://imagen.research.google/)和[Parti](https://parti.research.google/)团队提出。
+
+根据[Parti官方网站](https://parti.research.google/)说明:
+
+> PartiPrompts (P2)是我们发布的包含1600多个英文提示词的丰富集合,可用于测量模型在不同类别和挑战维度上的能力。
+
+
+
+PartiPrompts包含以下字段:
+- Prompt(提示词)
+- Category(类别,如"抽象"、"世界知识"等)
+- Challenge(难度等级,如"基础"、"复杂"、"文字与符号"等)
+
+这些基准测试支持对不同图像生成模型进行并排人工对比评估。为此,🧨 Diffusers团队构建了**Open Parti Prompts**——一个基于Parti Prompts的社区驱动型定性评估基准,用于比较顶尖开源diffusion模型:
+- [Open Parti Prompts游戏](https://huggingface.co/spaces/OpenGenAI/open-parti-prompts):展示10个parti提示词对应的4张生成图像,用户选择最符合提示的图片
+- [Open Parti Prompts排行榜](https://huggingface.co/spaces/OpenGenAI/parti-prompts-leaderboard):对比当前最优开源diffusion模型的性能榜单
+
+为进行手动图像对比,我们演示如何使用`diffusers`处理部分PartiPrompts提示词。
+
+以下是从不同挑战维度(基础、复杂、语言结构、想象力、文字与符号)采样的提示词示例(使用[PartiPrompts作为数据集](https://huggingface.co/datasets/nateraw/parti-prompts)):
+
+```python
+from datasets import load_dataset
+
+# prompts = load_dataset("nateraw/parti-prompts", split="train")
+# prompts = prompts.shuffle()
+# sample_prompts = [prompts[i]["Prompt"] for i in range(5)]
+
+# Fixing these sample prompts in the interest of reproducibility.
+sample_prompts = [
+ "a corgi",
+ "a hot air balloon with a yin-yang symbol, with the moon visible in the daytime sky",
+ "a car with no windows",
+ "a cube made of porcupine",
+ 'The saying "BE EXCELLENT TO EACH OTHER" written on a red brick wall with a graffiti image of a green alien wearing a tuxedo. A yellow fire hydrant is on a sidewalk in the foreground.',
+]
+```
+
+现在我们可以使用Stable Diffusion([v1-4 checkpoint](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4))生成这些提示词对应的图像:
+
+```python
+import torch
+
+seed = 0
+generator = torch.manual_seed(seed)
+
+images = sd_pipeline(sample_prompts, num_images_per_prompt=1, generator=generator).images
+```
+
+
+
+我们也可以通过设置`num_images_per_prompt`参数来比较同一提示词生成的不同图像。使用不同检查点([v1-5](https://huggingface.co/stable-diffusion-v1-5/stable-diffusion-v1-5))运行相同流程后,结果如下:
+
+
+
+当使用多个待评估模型为所有提示词生成若干图像后,这些结果将提交给人类评估员进行打分。有关DrawBench和PartiPrompts基准测试的更多细节,请参阅各自的论文。
+
+
+
+在模型训练过程中查看推理样本有助于评估训练进度。我们的[训练脚本](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/)支持此功能,并额外提供TensorBoard和Weights & Biases日志记录功能。
+
+
+
+## 定量评估
+
+本节将指导您如何评估三种不同的扩散流程,使用以下指标:
+- CLIP分数
+- CLIP方向相似度
+- FID(弗雷歇起始距离)
+
+### 文本引导图像生成
+
+[CLIP分数](https://huggingface.co/papers/2104.08718)用于衡量图像-标题对的匹配程度。CLIP分数越高表明匹配度越高🔼。该分数是对"匹配度"这一定性概念的量化测量,也可以理解为图像与标题之间的语义相似度。研究发现CLIP分数与人类判断具有高度相关性。
+
+首先加载[`StableDiffusionPipeline`]:
+
+```python
+from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
+import torch
+
+model_ckpt = "CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4"
+sd_pipeline = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_ckpt, torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
+```
+
+使用多个提示词生成图像:
+
+```python
+prompts = [
+ "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars",
+ "A high tech solarpunk utopia in the Amazon rainforest",
+ "A pikachu fine dining with a view to the Eiffel Tower",
+ "A mecha robot in a favela in expressionist style",
+ "an insect robot preparing a delicious meal",
+ "A small cabin on top of a snowy mountain in the style of Disney, artstation",
+]
+
+images = sd_pipeline(prompts, num_images_per_prompt=1, output_type="np").images
+
+print(images.shape)
+# (6, 512, 512, 3)
+```
+
+然后计算CLIP分数:
+
+```python
+from torchmetrics.functional.multimodal import clip_score
+from functools import partial
+
+clip_score_fn = partial(clip_score, model_name_or_path="openai/clip-vit-base-patch16")
+
+def calculate_clip_score(images, prompts):
+ images_int = (images * 255).astype("uint8")
+ clip_score = clip_score_fn(torch.from_numpy(images_int).permute(0, 3, 1, 2), prompts).detach()
+ return round(float(clip_score), 4)
+
+sd_clip_score = calculate_clip_score(images, prompts)
+print(f"CLIP分数: {sd_clip_score}")
+# CLIP分数: 35.7038
+```
+
+上述示例中,我们为每个提示生成一张图像。如果为每个提示生成多张图像,则需要计算每个提示生成图像的平均分数。
+
+当需要比较两个兼容[`StableDiffusionPipeline`]的检查点时,应在调用管道时传入生成器。首先使用[v1-4 Stable Diffusion检查点](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4)以固定种子生成图像:
+
+```python
+seed = 0
+generator = torch.manual_seed(seed)
+
+images = sd_pipeline(prompts, num_images_per_prompt=1, generator=generator, output_type="np").images
+```
+
+然后加载[v1-5检查点](https://huggingface.co/stable-diffusion-v1-5/stable-diffusion-v1-5)生成图像:
+
+```python
+model_ckpt_1_5 = "stable-diffusion-v1-5/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
+sd_pipeline_1_5 = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_ckpt_1_5, torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
+
+images_1_5 = sd_pipeline_1_5(prompts, num_images_per_prompt=1, generator=generator, output_type="np").images
+```
+
+最后比较两者的CLIP分数:
+
+```python
+sd_clip_score_1_4 = calculate_clip_score(images, prompts)
+print(f"v-1-4版本的CLIP分数: {sd_clip_score_1_4}")
+# v-1-4版本的CLIP分数: 34.9102
+
+sd_clip_score_1_5 = calculate_clip_score(images_1_5, prompts)
+print(f"v-1-5版本的CLIP分数: {sd_clip_score_1_5}")
+# v-1-5版本的CLIP分数: 36.2137
+```
+
+结果表明[v1-5](https://huggingface.co/stable-diffusion-v1-5/stable-diffusion-v1-5)检查点性能优于前代。但需注意,我们用于计算CLIP分数的提示词数量较少。实际评估时应使用更多样化且数量更大的提示词集。
+
+
+
+该分数存在固有局限性:训练数据中的标题是从网络爬取,并提取自图片关联的`alt`等标签。这些描述未必符合人类描述图像的方式,因此我们需要人工"设计"部分提示词。
+
+
+
+### 图像条件式文本生成图像
+
+这种情况下,生成管道同时接受输入图像和文本提示作为条件。以[`StableDiffusionInstructPix2PixPipeline`]为例,该管道接收编辑指令作为输入提示,并接受待编辑的输入图像。
+
+示例图示:
+
+
+
+评估此类模型的策略之一是测量两幅图像间变化的连贯性(通过[CLIP](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/clip)定义)中两个图像之间的变化与两个图像描述之间的变化的一致性(如论文[《CLIP-Guided Domain Adaptation of Image Generators》](https://huggingface.co/papers/2108.00946)所示)。这被称为“**CLIP方向相似度**”。
+
+- **描述1**对应输入图像(图像1),即待编辑的图像。
+- **描述2**对应编辑后的图像(图像2),应反映编辑指令。
+
+以下是示意图:
+
+
+
+我们准备了一个小型数据集来实现该指标。首先加载数据集:
+
+```python
+from datasets import load_dataset
+
+dataset = load_dataset("sayakpaul/instructpix2pix-demo", split="train")
+dataset.features
+```
+
+```bash
+{'input': Value(dtype='string', id=None),
+ 'edit': Value(dtype='string', id=None),
+ 'output': Value(dtype='string', id=None),
+ 'image': Image(decode=True, id=None)}
+```
+
+数据字段说明:
+
+- `input`:与`image`对应的原始描述。
+- `edit`:编辑指令。
+- `output`:反映`edit`指令的修改后描述。
+
+查看一个样本:
+
+```python
+idx = 0
+print(f"Original caption: {dataset[idx]['input']}")
+print(f"Edit instruction: {dataset[idx]['edit']}")
+print(f"Modified caption: {dataset[idx]['output']}")
+```
+
+```bash
+Original caption: 2. FAROE ISLANDS: An archipelago of 18 mountainous isles in the North Atlantic Ocean between Norway and Iceland, the Faroe Islands has 'everything you could hope for', according to Big 7 Travel. It boasts 'crystal clear waterfalls, rocky cliffs that seem to jut out of nowhere and velvety green hills'
+Edit instruction: make the isles all white marble
+Modified caption: 2. WHITE MARBLE ISLANDS: An archipelago of 18 mountainous white marble isles in the North Atlantic Ocean between Norway and Iceland, the White Marble Islands has 'everything you could hope for', according to Big 7 Travel. It boasts 'crystal clear waterfalls, rocky cliffs that seem to jut out of nowhere and velvety green hills'
+```
+
+对应的图像:
+
+```python
+dataset[idx]["image"]
+```
+
+
+
+我们将根据编辑指令修改数据集中的图像,并计算方向相似度。
+
+首先加载[`StableDiffusionInstructPix2PixPipeline`]:
+
+```python
+from diffusers import StableDiffusionInstructPix2PixPipeline
+
+instruct_pix2pix_pipeline = StableDiffusionInstructPix2PixPipeline.from_pretrained(
+ "timbrooks/instruct-pix2pix", torch_dtype=torch.float16
+).to("cuda")
+```
+
+执行编辑操作:
+
+```python
+import numpy as np
+
+
+def edit_image(input_image, instruction):
+ image = instruct_pix2pix_pipeline(
+ instruction,
+ image=input_image,
+ output_type="np",
+ generator=generator,
+ ).images[0]
+ return image
+
+input_images = []
+original_captions = []
+modified_captions = []
+edited_images = []
+
+for idx in range(len(dataset)):
+ input_image = dataset[idx]["image"]
+ edit_instruction = dataset[idx]["edit"]
+ edited_image = edit_image(input_image, edit_instruction)
+
+ input_images.append(np.array(input_image))
+ original_captions.append(dataset[idx]["input"])
+ modified_captions.append(dataset[idx]["output"])
+ edited_images.append(edited_image)
+```
+
+为测量方向相似度,我们首先加载CLIP的图像和文本编码器:
+
+```python
+from transformers import (
+ CLIPTokenizer,
+ CLIPTextModelWithProjection,
+ CLIPVisionModelWithProjection,
+ CLIPImageProcessor,
+)
+
+clip_id = "openai/clip-vit-large-patch14"
+tokenizer = CLIPTokenizer.from_pretrained(clip_id)
+text_encoder = CLIPTextModelWithProjection.from_pretrained(clip_id).to("cuda")
+image_processor = CLIPImageProcessor.from_pretrained(clip_id)
+image_encoder = CLIPVisionModelWithProjection.from_pretrained(clip_id).to("cuda")
+```
+
+注意我们使用的是特定CLIP检查点——`openai/clip-vit-large-patch14`,因为Stable Diffusion预训练正是基于此CLIP变体。详见[文档](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/clip)。
+
+接着准备计算方向相似度的PyTorch `nn.Module`:
+
+```python
+import torch.nn as nn
+import torch.nn.functional as F
+
+
+class DirectionalSimilarity(nn.Module):
+ def __init__(self, tokenizer, text_encoder, image_processor, image_encoder):
+ super().__init__()
+ self.tokenizer = tokenizer
+ self.text_encoder = text_encoder
+ self.image_processor = image_processor
+ self.image_encoder = image_encoder
+
+ def preprocess_image(self, image):
+ image = self.image_processor(image, return_tensors="pt")["pixel_values"]
+ return {"pixel_values": image.to("cuda")}
+
+ def tokenize_text(self, text):
+ inputs = self.tokenizer(
+ text,
+ max_length=self.tokenizer.model_max_length,
+ padding="max_length",
+ truncation=True,
+ return_tensors="pt",
+ )
+ return {"input_ids": inputs.input_ids.to("cuda")}
+
+ def encode_image(self, image):
+ preprocessed_image = self.preprocess_image(image)
+ image_features = self.image_encoder(**preprocessed_image).image_embeds
+ image_features = image_features / image_features.norm(dim=1, keepdim=True)
+ return image_features
+
+ def encode_text(self, text):
+ tokenized_text = self.tokenize_text(text)
+ text_features = self.text_encoder(**tokenized_text).text_embeds
+ text_features = text_features / text_features.norm(dim=1, keepdim=True)
+ return text_features
+
+ def compute_directional_similarity(self, img_feat_one, img_feat_two, text_feat_one, text_feat_two):
+ sim_direction = F.cosine_similarity(img_feat_two - img_feat_one, text_feat_two - text_feat_one)
+ return sim_direction
+
+ def forward(self, image_one, image_two, caption_one, caption_two):
+ img_feat_one = self.encode_image(image_one)
+ img_feat_two = self.encode_image(image_two)
+ text_feat_one = self.encode_text(caption_one)
+ text_feat_two = self.encode_text(caption_two)
+ directional_similarity = self.compute_directional_similarity(
+ img_feat_one, img_feat_two, text_feat_one, text_feat_two
+ )
+ return directional_similarity
+```
+
+现在让我们使用`DirectionalSimilarity`模块:
+
+```python
+dir_similarity = DirectionalSimilarity(tokenizer, text_encoder, image_processor, image_encoder)
+scores = []
+
+for i in range(len(input_images)):
+ original_image = input_images[i]
+ original_caption = original_captions[i]
+ edited_image = edited_images[i]
+ modified_caption = modified_captions[i]
+
+ similarity_score = dir_similarity(original_image, edited_image, original_caption, modified_caption)
+ scores.append(float(similarity_score.detach().cpu()))
+
+print(f"CLIP方向相似度: {np.mean(scores)}")
+# CLIP方向相似度: 0.0797976553440094
+```
+
+与CLIP分数类似,CLIP方向相似度数值越高越好。
+
+需要注意的是,`StableDiffusionInstructPix2PixPipeline`提供了两个控制参数`image_guidance_scale`和`guidance_scale`来调节最终编辑图像的质量。建议您尝试调整这两个参数,观察它们对方向相似度的影响。
+
+我们可以扩展这个度量标准来评估原始图像与编辑版本的相似度,只需计算`F.cosine_similarity(img_feat_two, img_feat_one)`。对于这类编辑任务,我们仍希望尽可能保留图像的主要语义特征(即保持较高的相似度分数)。
+
+该度量方法同样适用于类似流程,例如[`StableDiffusionPix2PixZeroPipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/pix2pix_zero#diffusers.StableDiffusionPix2PixZeroPipeline)。
+
+
+
+CLIP分数和CLIP方向相似度都依赖CLIP模型,可能导致评估结果存在偏差。
+
+
+
+***扩展IS、FID(后文讨论)或KID等指标存在困难***,当被评估模型是在大型图文数据集(如[LAION-5B数据集](https://laion.ai/blog/laion-5b/))上预训练时。因为这些指标的底层都使用了在ImageNet-1k数据集上预训练的InceptionNet来提取图像特征。Stable Diffusion的预训练数据集与InceptionNet的预训练数据集可能重叠有限,因此不适合作为特征提取器。
+
+***上述指标更适合评估类别条件模型***,例如[DiT](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/dit)。该模型是在ImageNet-1k类别条件下预训练的。
+这是9篇文档中的第8部分。
+
+### 基于类别的图像生成
+
+基于类别的生成模型通常是在带有类别标签的数据集(如[ImageNet-1k](https://huggingface.co/datasets/imagenet-1k))上进行预训练的。评估这些模型的常用指标包括Fréchet Inception Distance(FID)、Kernel Inception Distance(KID)和Inception Score(IS)。本文档重点介绍FID([Heusel等人](https://huggingface.co/papers/1706.08500)),并展示如何使用[`DiTPipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/pipelines/dit)计算该指标,该管道底层使用了[DiT模型](https://huggingface.co/papers/2212.09748)。
+
+FID旨在衡量两组图像数据集的相似程度。根据[此资源](https://mmgeneration.readthedocs.io/en/latest/quick_run.html#fid):
+
+> Fréchet Inception Distance是衡量两组图像数据集相似度的指标。研究表明其与人类对视觉质量的主观判断高度相关,因此最常用于评估生成对抗网络(GAN)生成样本的质量。FID通过计算Inception网络特征表示所拟合的两个高斯分布之间的Fréchet距离来实现。
+
+这两个数据集本质上是真实图像数据集和生成图像数据集(本例中为人工生成的图像)。FID通常基于两个大型数据集计算,但本文档将使用两个小型数据集进行演示。
+
+首先下载ImageNet-1k训练集中的部分图像:
+
+```python
+from zipfile import ZipFile
+import requests
+
+
+def download(url, local_filepath):
+ r = requests.get(url)
+ with open(local_filepath, "wb") as f:
+ f.write(r.content)
+ return local_filepath
+
+dummy_dataset_url = "https://hf.co/datasets/sayakpaul/sample-datasets/resolve/main/sample-imagenet-images.zip"
+local_filepath = download(dummy_dataset_url, dummy_dataset_url.split("/")[-1])
+
+with ZipFile(local_filepath, "r") as zipper:
+ zipper.extractall(".")
+```
+
+```python
+from PIL import Image
+import os
+import numpy as np
+
+dataset_path = "sample-imagenet-images"
+image_paths = sorted([os.path.join(dataset_path, x) for x in os.listdir(dataset_path)])
+
+real_images = [np.array(Image.open(path).convert("RGB")) for path in image_paths]
+```
+
+这些是来自以下ImageNet-1k类别的10张图像:"cassette_player"、"chain_saw"(2张)、"church"、"gas_pump"(3张)、"parachute"(2张)和"tench"。
+
+
+ 
+ 真实图像
+
+
+加载图像后,我们对其进行轻量级预处理以便用于FID计算:
+
+```python
+from torchvision.transforms import functional as F
+import torch
+
+
+def preprocess_image(image):
+ image = torch.tensor(image).unsqueeze(0)
+ image = image.permute(0, 3, 1, 2) / 255.0
+ return F.center_crop(image, (256, 256))
+
+real_images = torch.stack([dit_pipeline.preprocess_image(image) for image in real_images])
+print(real_images.shape)
+# torch.Size([10, 3, 256, 256])
+```
+
+我们现在加载[`DiTPipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/pipelines/dit)来生成基于上述类别的条件图像。
+
+```python
+from diffusers import DiTPipeline, DPMSolverMultistepScheduler
+
+dit_pipeline = DiTPipeline.from_pretrained("facebook/DiT-XL-2-256", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
+dit_pipeline.scheduler = DPMSolverMultistepScheduler.from_config(dit_pipeline.scheduler.config)
+dit_pipeline = dit_pipeline.to("cuda")
+
+seed = 0
+generator = torch.manual_seed(seed)
+
+
+words = [
+ "cassette player",
+ "chainsaw",
+ "chainsaw",
+ "church",
+ "gas pump",
+ "gas pump",
+ "gas pump",
+ "parachute",
+ "parachute",
+ "tench",
+]
+
+class_ids = dit_pipeline.get_label_ids(words)
+output = dit_pipeline(class_labels=class_ids, generator=generator, output_type="np")
+
+fake_images = output.images
+fake_images = torch.tensor(fake_images)
+fake_images = fake_images.permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
+print(fake_images.shape)
+# torch.Size([10, 3, 256, 256])
+```
+
+现在,我们可以使用[`torchmetrics`](https://torchmetrics.readthedocs.io/)计算FID分数。
+
+```python
+from torchmetrics.image.fid import FrechetInceptionDistance
+
+fid = FrechetInceptionDistance(normalize=True)
+fid.update(real_images, real=True)
+fid.update(fake_images, real=False)
+
+print(f"FID分数: {float(fid.compute())}")
+# FID分数: 177.7147216796875
+```
+
+FID分数越低越好。以下因素会影响FID结果:
+
+- 图像数量(包括真实图像和生成图像)
+- 扩散过程中引入的随机性
+- 扩散过程的推理步数
+- 扩散过程中使用的调度器
+
+对于最后两点,最佳实践是使用不同的随机种子和推理步数进行多次评估,然后报告平均结果。
+
+
+
+FID结果往往具有脆弱性,因为它依赖于许多因素:
+
+* 计算过程中使用的特定Inception模型
+* 计算实现的准确性
+* 图像格式(PNG和JPG的起点不同)
+
+需要注意的是,FID通常在比较相似实验时最有用,但除非作者仔细公开FID测量代码,否则很难复现论文结果。
+
+这些注意事项同样适用于其他相关指标,如KID和IS。
+
+
+
+最后,让我们可视化检查这些`fake_images`。
+
+
+ 
+ 生成图像示例
+
diff --git a/docs/source/zh/conceptual/philosophy.md b/docs/source/zh/conceptual/philosophy.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000000..581e582bba56
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/source/zh/conceptual/philosophy.md
@@ -0,0 +1,104 @@
+
+
+# 设计哲学
+
+🧨 Diffusers 提供**最先进**的预训练扩散模型支持多模态任务。
+其目标是成为推理和训练通用的**模块化工具箱**。
+
+我们致力于构建一个经得起时间考验的库,因此对API设计极为重视。
+
+简而言之,Diffusers 被设计为 PyTorch 的自然延伸。因此,我们的多数设计决策都基于 [PyTorch 设计原则](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/community/design.html#pytorch-design-philosophy)。以下是核心原则:
+
+## 可用性优先于性能
+
+- 尽管 Diffusers 包含众多性能优化特性(参见[内存与速度优化](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/optimization/fp16)),模型默认总是以最高精度和最低优化级别加载。因此除非用户指定,扩散流程(pipeline)默认在CPU上以float32精度初始化。这确保了跨平台和加速器的可用性,意味着运行本库无需复杂安装。
+- Diffusers 追求**轻量化**,仅有少量必需依赖,但提供诸多可选依赖以提升性能(如`accelerate`、`safetensors`、`onnx`等)。我们竭力保持库的轻量级特性,使其能轻松作为其他包的依赖项。
+- Diffusers 偏好简单、自解释的代码而非浓缩的"魔法"代码。这意味着lambda函数等简写语法和高级PyTorch操作符通常不被采用。
+
+## 简洁优于简易
+
+正如PyTorch所言:**显式优于隐式**,**简洁优于复杂**。这一哲学体现在库的多个方面:
+- 我们遵循PyTorch的API设计,例如使用[`DiffusionPipeline.to`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/diffusion_pipeline#diffusers.DiffusionPipeline.to)让用户自主管理设备。
+- 明确的错误提示优于静默纠正错误输入。Diffusers 旨在教育用户,而非单纯降低使用难度。
+- 暴露复杂的模型与调度器(scheduler)交互逻辑而非内部魔法处理。调度器/采样器与扩散模型分离且相互依赖最小化,迫使用户编写展开的去噪循环。但这种分离便于调试,并赋予用户更多控制权来调整去噪过程或切换模型/调度器。
+- 扩散流程中独立训练的组件(如文本编码器、UNet、变分自编码器)各有专属模型类。这要求用户处理组件间交互,且序列化格式将组件分存不同文件。但此举便于调试和定制,得益于组件分离,DreamBooth或Textual Inversion训练变得极为简单。
+
+## 可定制与贡献友好优于抽象
+
+库的大部分沿用了[Transformers库](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers)的重要设计原则:宁要重复代码,勿要仓促抽象。这一原则与[DRY原则](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Don%27t_repeat_yourself)形成鲜明对比。
+
+简言之,正如Transformers对建模文件的做法,Diffusers对流程(pipeline)和调度器(scheduler)保持极低抽象度与高度自包含代码。函数、长代码块甚至类可能在多文件中重复,初看像是糟糕的松散设计。但该设计已被Transformers证明极其成功,对社区驱动的开源机器学习库意义重大:
+- 机器学习领域发展迅猛,范式、模型架构和算法快速迭代,难以定义长效代码抽象。
+- ML从业者常需快速修改现有代码进行研究,因此偏好自包含代码而非多重抽象。
+- 开源库依赖社区贡献,必须构建易于参与的代码库。抽象度越高、依赖越复杂、可读性越差,贡献难度越大。过度抽象的库会吓退贡献者。若贡献不会破坏核心功能,不仅吸引新贡献者,也更便于并行审查和修改。
+
+Hugging Face称此设计为**单文件政策**——即某个类的几乎所有代码都应写在单一自包含文件中。更多哲学探讨可参阅[此博文](https://huggingface.co/blog/transformers-design-philosophy)。
+
+Diffusers对流程和调度器完全遵循该哲学,但对diffusion模型仅部分适用。原因在于多数扩散流程(如[DDPM](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/pipelines/ddpm)、[Stable Diffusion](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/overview#stable-diffusion-pipelines)、[unCLIP (DALL·E 2)](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/pipelines/unclip)和[Imagen](https://imagen.research.google/))都基于相同扩散模型——[UNet](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/models/unet2d-cond)。
+
+现在您应已理解🧨 Diffusers的设计理念🤗。我们力求在全库贯彻这些原则,但仍存在少数例外或欠佳设计。如有反馈,我们❤️欢迎在[GitHub提交](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=&template=feedback.md&title=)。
+
+## 设计哲学细节
+
+现在深入探讨设计细节。Diffusers主要包含三类:[流程(pipeline)](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/pipelines)、[模型](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/models)和[调度器(scheduler)](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/schedulers)。以下是各类的具体设计决策。
+
+### 流程(Pipelines)
+
+流程设计追求易用性(因此不完全遵循[*简洁优于简易*](#简洁优于简易)),不要求功能完备,应视为使用[模型](#模型)和[调度器](#调度器schedulers)进行推理的示例。
+
+遵循原则:
+- 采用单文件政策。所有流程位于src/diffusers/pipelines下的独立目录。一个流程文件夹对应一篇扩散论文/项目/发布。如[`src/diffusers/pipelines/stable-diffusion`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/stable_diffusion)可包含多个流程文件。若流程功能相似,可使用[# Copied from机制](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/125d783076e5bd9785beb05367a2d2566843a271/src/diffusers/pipelines/stable_diffusion/pipeline_stable_diffusion_img2img.py#L251)。
+- 所有流程继承[`DiffusionPipeline`]。
+- 每个流程由不同模型和调度器组件构成,这些组件记录于[`model_index.json`文件](https://huggingface.co/stable-diffusion-v1-5/stable-diffusion-v1-5/blob/main/model_index.json),可通过同名属性访问,并可用[`DiffusionPipeline.components`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/diffusion_pipeline#diffusers.DiffusionPipeline.components)在流程间共享。
+- 所有流程应能通过[`DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/diffusion_pipeline#diffusers.DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained)加载。
+- 流程**仅**用于推理。
+- 流程代码应具备高可读性、自解释性和易修改性。
+- 流程应设计为可相互构建,便于集成到高层API。
+- 流程**非**功能完备的用户界面。完整UI推荐[InvokeAI](https://github.com/invoke-ai/InvokeAI)、[Diffuzers](https://github.com/abhishekkrthakur/diffuzers)或[lama-cleaner](https://github.com/Sanster/lama-cleaner)。
+- 每个流程应通过唯一的`__call__`方法运行,且参数命名应跨流程统一。
+- 流程应以其解决的任务命名。
+- 几乎所有新diffusion流程都应在新文件夹/文件中实现。
+
+### 模型
+
+模型设计为可配置的工具箱,是[PyTorch Module类](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.Module.html)的自然延伸,仅部分遵循**单文件政策**。
+
+遵循原则:
+- 模型对应**特定架构类型**。如[`UNet2DConditionModel`]类适用于所有需要2D图像输入且受上下文调节的UNet变体。
+- 所有模型位于[`src/diffusers/models`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/models),每种架构应有独立文件,如[`unets/unet_2d_condition.py`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/models/unets/unet_2d_condition.py)、[`transformers/transformer_2d.py`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/models/transformers/transformer_2d.py)等。
+- 模型**不**采用单文件政策,应使用小型建模模块如[`attention.py`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/models/attention.py)、[`resnet.py`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/models/resnet.py)、[`embeddings.py`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/models/embeddings.py)等。**注意**:这与Transformers的建模文件截然不同,表明模型未完全遵循单文件政策。
+- 模型意图暴露复杂度(类似PyTorch的`Module`类),并提供明确错误提示。
+- 所有模型继承`ModelMixin`和`ConfigMixin`。
+- 当不涉及重大代码变更、保持向后兼容性且显著提升内存/计算效率时,可对模型进行性能优化。
+- 模型默认应具备最高精度和最低性能设置。
+- 若新模型检查点可归类为现有架构,应适配现有架构而非新建文件。仅当架构根本性不同时才创建新文件。
+- 模型设计应便于未来扩展。可通过限制公开函数参数、配置参数和"预见"变更实现。例如:优先采用可扩展的`string`类型参数而非布尔型`is_..._type`参数。对现有架构的修改应保持最小化。
+- 模型设计需在代码可读性与多检查点支持间权衡。多数情况下应适配现有类,但某些例外(如[UNet块](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/models/unets/unet_2d_blocks.py)和[注意力处理器](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/models/attention_processor.py))需新建类以保证长期可读性。
+
+### 调度器(Schedulers)
+
+调度器负责引导推理去噪过程及定义训练噪声计划。它们设计为独立的可加载配置类,严格遵循**单文件政策**。
+
+遵循原则:
+- 所有调度器位于[`src/diffusers/schedulers`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/schedulers)。
+- 调度器**禁止**从大型工具文件导入,必须保持高度自包含。
+- 一个调度器Python文件对应一种算法(如论文定义的算法)。
+- 若调度器功能相似,可使用`# Copied from`机制。
+- 所有调度器继承`SchedulerMixin`和`ConfigMixin`。
+- 调度器可通过[`ConfigMixin.from_config`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/configuration#diffusers.ConfigMixin.from_config)轻松切换(详见[此处](../using-diffusers/schedulers))。
+- 每个调度器必须包含`set_num_inference_steps`和`step`函数。在每次去噪过程前(即调用`step(...)`前)必须调用`set_num_inference_steps(...)`。
+- 每个调度器通过`timesteps`属性暴露需要"循环"的时间步,这是模型将被调用的时间步数组。
+- `step(...)`函数接收模型预测输出和"当前"样本(x_t),返回"前一个"略去噪的样本(x_t-1)。
+- 鉴于扩散调度器的复杂性,`step`函数不暴露全部细节,可视为"黑盒"。
+- 几乎所有新调度器都应在新文件中实现。
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/source/zh/optimization/fp16.md b/docs/source/zh/optimization/fp16.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000000..1088482d2432
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/source/zh/optimization/fp16.md
@@ -0,0 +1,307 @@
+
+
+# 加速推理
+
+Diffusion模型在推理时速度较慢,因为生成是一个迭代过程,需要经过一定数量的"步数"逐步将噪声细化为图像或视频。要加速这一过程,您可以尝试使用不同的[调度器](../api/schedulers/overview)、降低模型权重的精度以加快计算、使用更高效的内存注意力机制等方法。
+
+将这些技术组合使用,可以比单独使用任何一种技术获得更快的推理速度。
+
+本指南将介绍如何加速推理。
+
+## 模型数据类型
+
+模型权重的精度和数据类型会影响推理速度,因为更高的精度需要更多内存来加载,也需要更多时间进行计算。PyTorch默认以float32或全精度加载模型权重,因此更改数据类型是快速获得更快推理速度的简单方法。
+
+
+
+
+bfloat16与float16类似,但对数值误差更稳健。硬件对bfloat16的支持各不相同,但大多数现代GPU都能支持bfloat16。
+
+```py
+import torch
+from diffusers import StableDiffusionXLPipeline
+
+pipeline = StableDiffusionXLPipeline.from_pretrained(
+ "stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16
+).to("cuda")
+
+prompt = "Astronaut in a jungle, cold color palette, muted colors, detailed, 8k"
+pipeline(prompt, num_inference_steps=30).images[0]
+```
+
+
+
+
+float16与bfloat16类似,但可能更容易出现数值误差。
+
+```py
+import torch
+from diffusers import StableDiffusionXLPipeline
+
+pipeline = StableDiffusionXLPipeline.from_pretrained(
+ "stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16
+).to("cuda")
+
+prompt = "Astronaut in a jungle, cold color palette, muted colors, detailed, 8k"
+pipeline(prompt, num_inference_steps=30).images[0]
+```
+
+
+
+
+[TensorFloat-32 (tf32)](https://blogs.nvidia.com/blog/2020/05/14/tensorfloat-32-precision-format/)模式在NVIDIA Ampere GPU上受支持,它以tf32计算卷积和矩阵乘法运算。存储和其他操作保持在float32。与bfloat16或float16结合使用时,可以显著加快计算速度。
+
+PyTorch默认仅对卷积启用tf32模式,您需要显式启用矩阵乘法的tf32模式。
+
+```py
+import torch
+from diffusers import StableDiffusionXLPipeline
+
+torch.backends.cuda.matmul.allow_tf32 = True
+
+pipeline = StableDiffusionXLPipeline.from_pretrained(
+ "stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16
+).to("cuda")
+
+prompt = "Astronaut in a jungle, cold color palette, muted colors, detailed, 8k"
+pipeline(prompt, num_inference_steps=30).images[0]
+```
+
+更多详情请参阅[混合精度训练](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/en/perf_train_gpu_one#mixed-precision)文档。
+
+
+
+
+## 缩放点积注意力
+
+> [!TIP]
+> 内存高效注意力优化了推理速度*和*[内存使用](./memory#memory-efficient-attention)!
+
+[缩放点积注意力(SDPA)](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention.html)实现了多种注意力后端,包括[FlashAttention](https://github.com/Dao-AILab/flash-attention)、[xFormers](https://github.com/facebookresearch/xformers)和原生C++实现。它会根据您的硬件自动选择最优的后端。
+
+如果您使用的是PyTorch >= 2.0,SDPA默认启用,无需对代码进行任何额外更改。不过,您也可以尝试使用其他注意力后端来自行选择。下面的示例使用[torch.nn.attention.sdpa_kernel](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.attention.sdpa_kernel.html)上下文管理器来启用高效注意力。
+
+```py
+from torch.nn.attention import SDPBackend, sdpa_kernel
+import torch
+from diffusers import StableDiffusionXLPipeline
+
+pipeline = StableDiffusionXLPipeline.from_pretrained(
+ "stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16
+).to("cuda")
+
+prompt = "Astronaut in a jungle, cold color palette, muted colors, detailed, 8k"
+
+with sdpa_kernel(SDPBackend.EFFICIENT_ATTENTION):
+ image = pipeline(prompt, num_inference_steps=30).images[0]
+```
+
+## torch.compile
+
+[torch.compile](https://pytorch.org/tutorials/intermediate/torch_compile_tutorial.html)通过将PyTorch代码和操作编译为优化的内核来加速推理。Diffusers通常会编译计算密集型的模型,如UNet、transformer或VAE。
+
+启用以下编译器设置以获得最大速度(更多选项请参阅[完整列表](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/main/torch/_inductor/config.py))。
+
+```py
+import torch
+from diffusers import StableDiffusionXLPipeline
+
+torch._inductor.config.conv_1x1_as_mm = True
+torch._inductor.config.coordinate_descent_tuning = True
+torch._inductor.config.epilogue_fusion = False
+torch._inductor.config.coordinate_descent_check_all_directions = True
+```
+
+加载并编译UNet和VAE。有几种不同的模式可供选择,但`"max-autotune"`通过编译为CUDA图来优化速度。CUDA图通过单个CPU操作启动多个GPU操作,有效减少了开销。
+
+> [!TIP]
+> 在PyTorch 2.3.1中,您可以控制torch.compile的缓存行为。这对于像`"max-autotune"`这样的编译模式特别有用,它会通过网格搜索多个编译标志来找到最优配置。更多详情请参阅[torch.compile中的编译时间缓存](https://pytorch.org/tutorials/recipes/torch_compile_caching_tutorial.html)教程。
+
+将内存布局更改为[channels_last](./memory#torchchannels_last)也可以优化内存和推理速度。
+
+```py
+pipeline = StableDiffusionXLPipeline.from_pretrained(
+ "stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16
+).to("cuda")
+pipeline.unet.to(memory_format=torch.channels_last)
+pipeline.vae.to(memory_format=torch.channels_last)
+pipeline.unet = torch.compile(
+ pipeline.unet, mode="max-autotune", fullgraph=True
+)
+pipeline.vae.decode = torch.compile(
+ pipeline.vae.decode,
+ mode="max-autotune",
+ fullgraph=True
+)
+
+prompt = "Astronaut in a jungle, cold color palette, muted colors, detailed, 8k"
+pipeline(prompt, num_inference_steps=30).images[0]
+```
+
+第一次编译时速度较慢,但一旦编译完成,速度会显著提升。尽量只在相同类型的推理操作上使用编译后的管道。在不同尺寸的图像上调用编译后的管道会重新触发编译,这会很慢且效率低下。
+
+### 动态形状编译
+
+> [!TIP]
+> 确保始终使用PyTorch的nightly版本以获得更好的支持。
+
+`torch.compile`会跟踪输入形状和条件,如果这些不同,它会重新编译模型。例如,如果模型是在1024x1024分辨率的图像上编译的,而在不同分辨率的图像上使用,就会触发重新编译。
+
+为避免重新编译,添加`dynamic=True`以尝试生成更动态的内核,避免条件变化时重新编译。
+
+```diff
++ torch.fx.experimental._config.use_duck_shape = False
++ pipeline.unet = torch.compile(
+ pipeline.unet, fullgraph=True, dynamic=True
+)
+```
+
+指定`use_duck_shape=False`会指示编译器是否应使用相同的符号变量来表示相同大小的输入。更多详情请参阅此[评论](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/pull/11327#discussion_r2047659790)。
+
+并非所有模型都能开箱即用地从动态编译中受益,可能需要更改。参考此[PR](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/pull/11297/),它改进了[`AuraFlowPipeline`]的实现以受益于动态编译。
+
+如果动态编译对Diffusers模型的效果不如预期,请随时提出问题。
+
+### 区域编译
+
+[区域编译](https://docs.pytorch.org/tutorials/recipes/regional_compilation.html)通过仅编译模型中*小而频繁重复的块*(通常是transformer层)来减少冷启动延迟,并为每个后续出现的块重用编译后的工件。对于许多diffusion架构,这提供了与全图编译相同的运行时加速,并将编译时间减少了8-10倍。
+
+使用[`~ModelMixin.compile_repeated_blocks`]方法(一个包装`torch.compile`的辅助函数)在任何组件(如transformer模型)上,如下所示。
+
+```py
+# pip install -U diffusers
+import torch
+from diffusers import StableDiffusionXLPipeline
+
+pipeline = StableDiffusionXLPipeline.from_pretrained(
+ "stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0",
+ torch_dtype=torch.float16,
+).to("cuda")
+
+# 仅编译UNet中重复的transformer层
+pipeline.unet.compile_repeated_blocks(fullgraph=True)
+```
+
+要为新模型启用区域编译,请在模型类中添加一个`_repeated_blocks`属性,包含您想要编译的块的类名(作为字符串)。
+
+```py
+class MyUNet(ModelMixin):
+ _repeated_blocks = ("Transformer2DModel",) # ← 默认编译
+```
+
+> [!TIP]
+> 更多区域编译示例,请参阅参考[PR](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/pull/11705)。
+
+[Accelerate](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate/index)中还有一个[compile_regions](https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate/blob/273799c85d849a1954a4f2e65767216eb37fa089/src/accelerate/utils/other.py#L78)方法,可以自动选择模型中的候选块进行编译。其余图会单独编译。这对于快速实验很有用,因为您不需要设置哪些块要编译或调整编译标志。
+
+```py
+# pip install -U accelerate
+import torch
+from diffusers import StableDiffusionXLPipeline
+from accelerate.utils import compile regions
+
+pipeline = StableDiffusionXLPipeline.from_pretrained(
+ "stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16
+).to("cuda")
+pipeline.unet = compile_regions(pipeline.unet, mode="reduce-overhead", fullgraph=True)
+```
+
+[`~ModelMixin.compile_repeated_blocks`]是故意显式的。在`_repeated_blocks`中列出要重复的块,辅助函数仅编译这些块。它提供了可预测的行为,并且只需一行代码即可轻松推理缓存重用。
+
+### 图中断
+
+在torch.compile中指定`fullgraph=True`非常重要,以确保底层模型中没有图中断。这使您可以充分利用torch.compile而不会降低性能。对于UNet和VAE,这会改变您访问返回变量的方式。
+
+```diff
+- latents = unet(
+- latents, timestep=timestep, encoder_hidden_states=prompt_embeds
+-).sample
+
++ latents = unet(
++ latents, timestep=timestep, encoder_hidden_states=prompt_embeds, return_dict=False
++)[0]
+```
+
+### GPU同步
+
+每次去噪器做出预测后,调度器的`step()`函数会被[调用](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/1d686bac8146037e97f3fd8c56e4063230f71751/src/diffusers/pipelines/stable_diffusion_xl/pipeline_stable_diffusion_xl.py#L1228),并且`sigmas`变量会被[索引](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/1d686bac8146037e97f3fd8c56e4063230f71751/src/diffusers/schedulers/scheduling_euler_discrete.py#L476)。当放在GPU上时,这会引入延迟,因为CPU和GPU之间需要进行通信同步。当去噪器已经编译时,这一点会更加明显。
+
+一般来说,`sigmas`应该[保持在CPU上](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/35a969d297cba69110d175ee79c59312b9f49e1e/src/diffusers/schedulers/scheduling_euler_discrete.py#L240),以避免通信同步和延迟。
+
+
+
+参阅[torch.compile和Diffusers:峰值性能实践指南](https://pytorch.org/blog/torch-compile-and-diffusers-a-hands-on-guide-to-peak-performance/)博客文章,了解如何为扩散模型最大化`torch.compile`的性能。
+
+
+
+### 基准测试
+
+参阅[diffusers/benchmarks](https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/benchmarks)数据集,查看编译管道的推理延迟和内存使用数据。
+
+[diffusers-torchao](https://github.com/sayakpaul/diffusers-torchao#benchmarking-results)仓库还包含Flux和CogVideoX编译版本的基准测试结果。
+
+## 动态量化
+
+[动态量化](https://pytorch.org/tutorials/recipes/recipes/dynamic_quantization.html)通过降低精度以加快数学运算来提高推理速度。这种特定类型的量化在运行时根据数据确定如何缩放激活,而不是使用固定的缩放因子。因此,缩放因子与数据更准确地匹配。
+
+以下示例使用[torchao](../quantization/torchao)库对UNet和VAE应用[动态int8量化](https://pytorch.org/tutorials/recipes/recipes/dynamic_quantization.html)。
+
+> [!TIP]
+> 参阅我们的[torchao](../quantization/torchao)文档,了解更多关于如何使用Diffusers torchao集成的信息。
+
+配置编译器标志以获得最大速度。
+
+```py
+import torch
+from torchao import apply_dynamic_quant
+from diffusers import StableDiffusionXLPipeline
+
+torch._inductor.config.conv_1x1_as_mm = True
+torch._inductor.config.coordinate_descent_tuning = True
+torch._inductor.config.epilogue_fusion = False
+torch._inductor.config.coordinate_descent_check_all_directions = True
+torch._inductor.config.force_fuse_int_mm_with_mul = True
+torch._inductor.config.use_mixed_mm = True
+```
+
+使用[dynamic_quant_filter_fn](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusion-fast/blob/0f169640b1db106fe6a479f78c1ed3bfaeba3386/utils/pipeline_utils.py#L16)过滤掉UNet和VAE中一些不会从动态量化中受益的线性层。
+
+```py
+pipeline = StableDiffusionXLPipeline.from_pretrained(
+ "stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16
+).to("cuda")
+
+apply_dynamic_quant(pipeline.unet, dynamic_quant_filter_fn)
+apply_dynamic_quant(pipeline.vae, dynamic_quant_filter_fn)
+
+prompt = "Astronaut in a jungle, cold color palette, muted colors, detailed, 8k"
+pipeline(prompt, num_inference_steps=30).images[0]
+```
+
+## 融合投影矩阵
+
+> [!WARNING]
+> [fuse_qkv_projections](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/58431f102cf39c3c8a569f32d71b2ea8caa461e1/src/diffusers/pipelines/pipeline_utils.py#L2034)方法是实验性的,目前主要支持Stable Diffusion管道。参阅此[PR](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/pull/6179)了解如何为其他管道启用它。
+
+在注意力块中,输入被投影到三个子空间,分别由投影矩阵Q、K和V表示。这些投影通常单独计算,但您可以水平组合这些矩阵为一个矩阵,并在单步中执行投影。这会增加输入投影的矩阵乘法大小,并提高量化的效果。
+
+```py
+pipeline.fuse_qkv_projections()
+```
+
+## 资源
+
+- 阅读[Presenting Flux Fast: Making Flux go brrr on H100s](https://pytorch.org/blog/presenting-flux-fast-making-flux-go-brrr-on-h100s/)博客文章,了解如何结合所有这些优化与[TorchInductor](https://docs.pytorch.org/docs/stable/torch.compiler.html)和[AOTInductor](https://docs.pytorch.org/docs/stable/torch.compiler_aot_inductor.html),使用[flux-fast](https://github.com/huggingface/flux-fast)的配方获得约2.5倍的加速。
+
+ 这些配方支持AMD硬件和[Flux.1 Kontext Dev](https://huggingface.co/black-forest-labs/FLUX.1-Kontext-dev)。
+- 阅读[torch.compile和Diffusers:峰值性能实践指南](https://pytorch.org/blog/torch-compile-and-diffusers-a-hands-on-guide-to-peak-performance/)博客文章,了解如何在使用`torch.compile`时最大化性能。
diff --git a/docs/source/zh/optimization/onnx.md b/docs/source/zh/optimization/onnx.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000000..4b3804d01500
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/source/zh/optimization/onnx.md
@@ -0,0 +1,82 @@
+
+
+# ONNX Runtime
+
+🤗 [Optimum](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum) 提供了兼容 ONNX Runtime 的 Stable Diffusion 流水线。您需要运行以下命令安装支持 ONNX Runtime 的 🤗 Optimum:
+
+```bash
+pip install -q optimum["onnxruntime"]
+```
+
+本指南将展示如何使用 ONNX Runtime 运行 Stable Diffusion 和 Stable Diffusion XL (SDXL) 流水线。
+
+## Stable Diffusion
+
+要加载并运行推理,请使用 [`~optimum.onnxruntime.ORTStableDiffusionPipeline`]。若需加载 PyTorch 模型并实时转换为 ONNX 格式,请设置 `export=True`:
+
+```python
+from optimum.onnxruntime import ORTStableDiffusionPipeline
+
+model_id = "stable-diffusion-v1-5/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
+pipeline = ORTStableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_id, export=True)
+prompt = "sailing ship in storm by Leonardo da Vinci"
+image = pipeline(prompt).images[0]
+pipeline.save_pretrained("./onnx-stable-diffusion-v1-5")
+```
+
+
+
+当前批量生成多个提示可能会占用过高内存。在问题修复前,建议采用迭代方式而非批量处理。
+
+
+
+如需离线导出 ONNX 格式流水线供后续推理使用,请使用 [`optimum-cli export`](https://huggingface.co/docs/optimum/main/en/exporters/onnx/usage_guides/export_a_model#exporting-a-model-to-onnx-using-the-cli) 命令:
+
+```bash
+optimum-cli export onnx --model stable-diffusion-v1-5/stable-diffusion-v1-5 sd_v15_onnx/
+```
+
+随后进行推理时(无需再次指定 `export=True`):
+
+```python
+from optimum.onnxruntime import ORTStableDiffusionPipeline
+
+model_id = "sd_v15_onnx"
+pipeline = ORTStableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_id)
+prompt = "sailing ship in storm by Leonardo da Vinci"
+image = pipeline(prompt).images[0]
+```
+
+
+

+
+
+
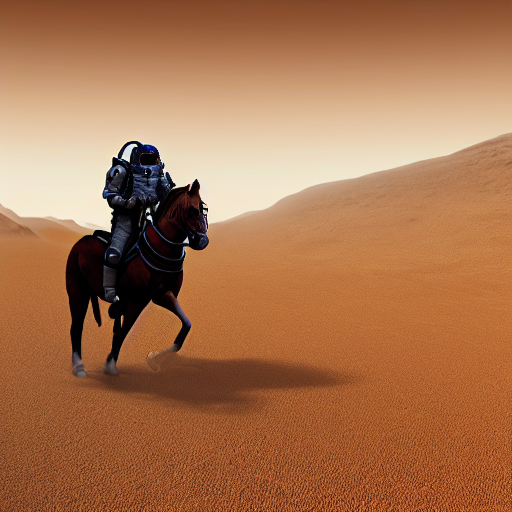

+
LMSDiscreteScheduler
+
+
+
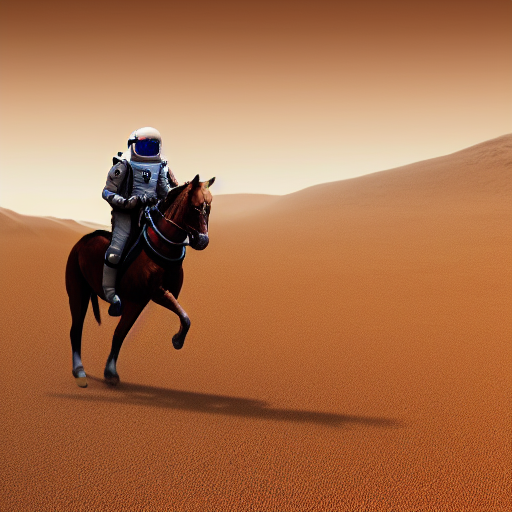

+
EulerDiscreteScheduler
+
+
+
+
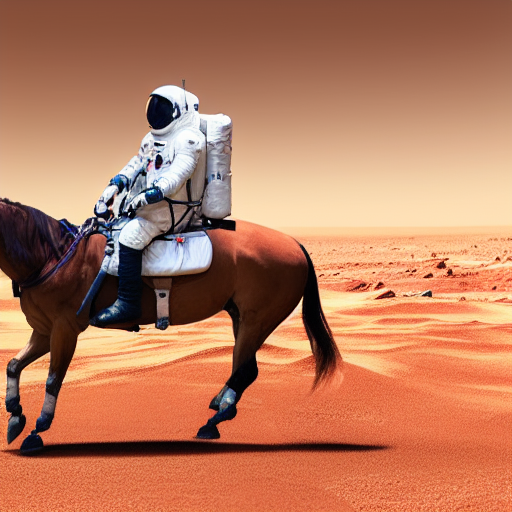

+
EulerAncestralDiscreteScheduler
+
+
+
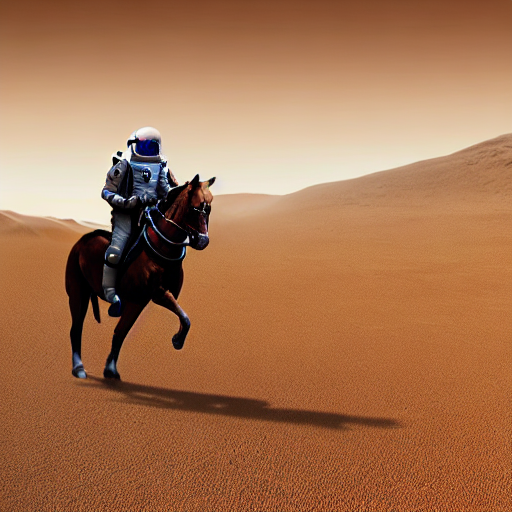

+
DPMSolverMultistepScheduler
+
+


 +
+ +
+ +
+  +
+  +
+  +
+  +
+  +
+  +
+  +
+  +
+无论您选择以何种方式贡献,我们都致力于成为一个开放、友好、善良的社区。请阅读我们的[行为准则](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md),并在互动时注意遵守。我们也建议您了解指导本项目的[伦理准则](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/conceptual/ethical_guidelines),并请您遵循同样的透明度和责任原则。
+
+我们高度重视社区的反馈,所以如果您认为自己有能帮助改进库的有价值反馈,请不要犹豫说出来——每条消息、评论、issue和拉取请求(PR)都会被阅读和考虑。
+
+## 概述
+
+您可以通过多种方式做出贡献,从在issue和讨论区回答问题,到向核心库添加新的diffusion模型。
+
+下面我们按难度升序列出不同的贡献方式,所有方式对社区都很有价值:
+
+* 1. 在[Diffusers讨论论坛](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers)或[Discord](https://discord.gg/G7tWnz98XR)上提问和回答问题
+* 2. 在[GitHub Issues标签页](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new/choose)提交新issue,或在[GitHub Discussions标签页](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/discussions/new/choose)发起新讨论
+* 3. 在[GitHub Issues标签页](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues)解答issue,或在[GitHub Discussions标签页](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/discussions)参与讨论
+* 4. 解决标记为"Good first issue"的简单问题,详见[此处](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22good+first+issue%22)
+* 5. 参与[文档](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/docs/source)建设
+* 6. 贡献[社区Pipeline](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3Acommunity-examples)
+* 7. 完善[示例代码](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples)
+* 8. 解决标记为"Good second issue"的中等难度问题,详见[此处](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22Good+second+issue%22)
+* 9. 添加新pipeline/模型/调度器,参见["New Pipeline/Model"](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22New+pipeline%2Fmodel%22)和["New scheduler"](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22New+scheduler%22)类issue。此类贡献请先阅读[设计哲学](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/PHILOSOPHY.md)
+
+重申:**所有贡献对社区都具有重要价值。**下文将详细说明各类贡献方式。
+
+对于4-9类贡献,您需要提交PR(拉取请求),具体操作详见[如何提交PR](#how-to-open-a-pr)章节。
+
+### 1. 在Diffusers讨论区或Discord提问与解答
+
+任何与Diffusers库相关的问题或讨论都可以发布在[官方论坛](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers/)或[Discord频道](https://discord.gg/G7tWnz98XR),包括但不限于:
+- 分享训练/推理实验报告
+- 展示个人项目
+- 咨询非官方训练示例
+- 项目提案
+- 通用反馈
+- 论文解读
+- 基于Diffusers库的个人项目求助
+- 一般性问题
+- 关于diffusion模型的伦理讨论
+- ...
+
+论坛/Discord上的每个问题都能促使社区公开分享知识,很可能帮助未来遇到相同问题的初学者。请务必提出您的疑问。
+同样地,通过回答问题您也在为社区创造公共知识文档,这种贡献极具价值。
+
+**请注意**:提问/回答时投入的精力越多,产生的公共知识质量就越高。精心构建的问题与专业解答能形成高质量知识库,而表述不清的问题则可能降低讨论价值。
+
+低质量的问题或回答会降低公共知识库的整体质量。
+简而言之,高质量的问题或回答应具备*精确性*、*简洁性*、*相关性*、*易于理解*、*可访问性*和*格式规范/表述清晰*等特质。更多详情请参阅[如何提交优质议题](#how-to-write-a-good-issue)章节。
+
+**关于渠道的说明**:
+[*论坛*](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers/63)的内容能被谷歌等搜索引擎更好地收录,且帖子按热度而非时间排序,便于查找历史问答。此外,论坛内容更容易被直接链接引用。
+而*Discord*采用即时聊天模式,适合快速交流。虽然在Discord上可能更快获得解答,但信息会随时间淹没,且难以回溯历史讨论。因此我们强烈建议在论坛发布优质问答,以构建可持续的社区知识库。若Discord讨论产生有价值结论,建议将成果整理发布至论坛以惠及更多读者。
+
+### 2. 在GitHub议题页提交新议题
+
+🧨 Diffusers库的稳健性离不开用户的问题反馈,感谢您的报错。
+
+请注意:GitHub议题仅限处理与Diffusers库代码直接相关的技术问题、错误报告、功能请求或库设计反馈。
+简言之,**与Diffusers库代码(含文档)无关**的内容应发布至[论坛](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers/63)或[Discord](https://discord.gg/G7tWnz98XR)。
+
+**提交新议题时请遵循以下准则**:
+- 确认是否已有类似议题(使用GitHub议题页的搜索栏)
+- 请勿在现有议题下追加新问题。若存在高度关联议题,应新建议题并添加相关链接
+- 确保使用英文提交。非英语用户可通过[DeepL](https://www.deepl.com/translator)等免费工具翻译
+- 检查升级至最新Diffusers版本是否能解决问题。提交前请确认`python -c "import diffusers; print(diffusers.__version__)"`显示的版本号不低于最新版本
+- 记请记住,你在提交新issue时投入的精力越多,得到的回答质量就越高,Diffusers项目的整体issue质量也会越好。
+
+新issue通常包含以下内容:
+
+#### 2.1 可复现的最小化错误报告
+
+错误报告应始终包含可复现的代码片段,并尽可能简洁明了。具体而言:
+- 尽量缩小问题范围,**不要直接粘贴整个代码文件**
+- 规范代码格式
+- 除Diffusers依赖库外,不要包含其他外部库
+- **务必**提供环境信息:可在终端运行`diffusers-cli env`命令,然后将显示的信息复制到issue中
+- 详细说明问题。如果读者不清楚问题所在及其影响,就无法解决问题
+- **确保**读者能以最小成本复现问题。如果代码片段因缺少库或未定义变量而无法运行,读者将无法提供帮助。请确保提供的可复现代码尽可能精简,可直接复制到Python shell运行
+- 如需特定模型/数据集复现问题,请确保读者能获取这些资源。可将模型/数据集上传至[Hub](https://huggingface.co)便于下载。尽量保持模型和数据集体积最小化,降低复现难度
+
+更多信息请参阅[如何撰写优质issue](#how-to-write-a-good-issue)章节。
+
+提交错误报告请点击[此处](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=bug&projects=&template=bug-report.yml)。
+
+#### 2.2 功能请求
+
+优质的功能请求应包含以下要素:
+
+1. 首先说明动机:
+* 是否与库的使用痛点相关?若是,请解释原因,最好提供演示问题的代码片段
+* 是否因项目需求产生?我们很乐意了解详情!
+* 是否是你已实现且认为对社区有价值的功能?请说明它为你解决了什么问题
+2. 用**完整段落**描述功能特性
+3. 提供**代码片段**演示预期用法
+4. 如涉及论文,请附上链接
+5. 可补充任何有助于理解的辅助材料(示意图、截图等)
+
+提交功能请求请点击[此处](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=&template=feature_request.md&title=)。
+
+#### 2.3 设计反馈
+
+关于库设计的反馈(无论正面还是负面)能极大帮助核心维护者打造更友好的库。要了解当前设计理念,请参阅[此文档](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/conceptual/philosophy)如果您认为某个设计选择与当前理念不符,请说明原因及改进建议。如果某个设计选择因过度遵循理念而限制了使用场景,也请解释原因并提出调整方案。
+若某个设计对您特别实用,请同样留下备注——这对未来的设计决策极具参考价值。
+
+您可通过[此链接](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=&template=feedback.md&title=)提交设计反馈。
+
+#### 2.4 技术问题
+
+技术问题主要涉及库代码的实现逻辑或特定功能模块的作用。提问时请务必:
+- 附上相关代码链接
+- 详细说明难以理解的具体原因
+
+技术问题提交入口:[点击此处](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=bug&template=bug-report.yml)
+
+#### 2.5 新模型/调度器/pipeline提案
+
+若diffusion模型社区发布了您希望集成到Diffusers库的新模型、pipeline或调度器,请提供以下信息:
+* 简要说明并附论文或发布链接
+* 开源实现链接(如有)
+* 模型权重下载链接(如已公开)
+
+若您愿意参与开发,请告知我们以便指导。另请尝试通过GitHub账号标记原始组件作者。
+
+提案提交地址:[新建请求](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=New+model%2Fpipeline%2Fscheduler&template=new-model-addition.yml)
+
+### 3. 解答GitHub问题
+
+回答GitHub问题可能需要Diffusers的技术知识,但我们鼓励所有人尝试参与——即使您对答案不完全正确。高质量回答的建议:
+- 保持简洁精炼
+- 严格聚焦问题本身
+- 提供代码/论文等佐证材料
+- 优先用代码说话:若代码片段能解决问题,请提供完整可复现代码
+
+许多问题可能存在离题、重复或无关情况。您可以通过以下方式协助维护者:
+- 引导提问者精确描述问题
+- 标记重复issue并附原链接
+- 推荐用户至[论坛](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers/63)或[Discord](https://discord.gg/G7tWnz98XR)
+
+在确认提交的Bug报告正确且需要修改源代码后,请继续阅读以下章节内容。
+
+以下所有贡献都需要提交PR(拉取请求)。具体操作步骤详见[如何提交PR](#how-to-open-a-pr)章节。
+
+### 4. 修复"Good first issue"类问题
+
+标有[Good first issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22good+first+issue%22)标签的问题通常已说明解决方案建议,便于修复。若该问题尚未关闭且您想尝试解决,只需留言"我想尝试解决这个问题"。通常有三种情况:
+- a.) 问题描述已提出解决方案。若您认可该方案,可直接提交PR或草稿PR进行修复
+- b.) 问题描述未提出解决方案。您可询问修复建议,Diffusers团队会尽快回复。若有成熟解决方案,也可直接提交PR
+- c.) 已有PR但问题未关闭。若原PR停滞,可新开PR并关联原PR(开源社区常见现象)。若PR仍活跃,您可通过建议、审查或协作等方式帮助原作者
+
+### 5. 文档贡献
+
+优秀库**必然**拥有优秀文档!官方文档是新用户的首要接触点,因此文档贡献具有**极高价值**。贡献形式包括:
+- 修正拼写/语法错误
+- 修复文档字符串格式错误(如显示异常或链接失效)
+- 修正文档字符串中张量的形状/维度描述
+- 优化晦涩或错误的说明
+- 更新过时代码示例
+- 文档翻译
+
+[官方文档页面](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/index)所有内容均属可修改范围,对应[文档源文件](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/docs/source)可进行编辑。修改前请查阅[验证说明](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/docs)。
+
+### 6. 贡献社区流程
+
+> [!TIP]
+> 阅读[社区流程](../using-diffusers/custom_pipeline_overview#community-pipelines)指南了解GitHub与Hugging Face Hub社区流程的区别。若想了解我们设立社区流程的原因,请查看GitHub Issue [#841](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/841)(简而言之,我们无法维护diffusion模型所有可能的推理使用方式,但也不希望限制社区构建这些流程)。
+
+贡献社区流程是向社区分享创意与成果的绝佳方式。您可以在[`DiffusionPipeline`]基础上构建流程,任何人都能通过设置`custom_pipeline`参数加载使用。本节将指导您创建一个简单的"单步"流程——UNet仅执行单次前向传播并调用调度器一次。
+
+1. 为社区流程创建one_step_unet.py文件。只要用户已安装相关包,该文件可包含任意所需包。确保仅有一个继承自[`DiffusionPipeline`]的流程类,用于从Hub加载模型权重和调度器配置。在`__init__`函数中添加UNet和调度器。
+
+ 同时添加`register_modules`函数,确保您的流程及其组件可通过[`~DiffusionPipeline.save_pretrained`]保存。
+
+```py
+from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
+import torch
+
+class UnetSchedulerOneForwardPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
+ def __init__(self, unet, scheduler):
+ super().__init__()
+
+ self.register_modules(unet=unet, scheduler=scheduler)
+```
+
+2. 在前向传播中(建议定义为`__call__`),可添加任意功能。对于"单步"流程,创建随机图像并通过设置`timestep=1`调用UNet和调度器一次。
+
+```py
+ from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
+ import torch
+
+ class UnetSchedulerOneForwardPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
+ def __init__(self, unet, scheduler):
+ super().__init__()
+
+ self.register_modules(unet=unet, scheduler=scheduler)
+
+ def __call__(self):
+ image = torch.randn(
+ (1, self.unet.config.in_channels, self.unet.config.sample_size, self.unet.config.sample_size),
+ )
+ timestep = 1
+
+ model_output = self.unet(image, timestep).sample
+ scheduler_output = self.scheduler.step(model_output, timestep, image).prev_sample
+
+ return scheduler_output
+```
+
+现在您可以通过传入UNet和调度器来运行流程,若流程结构相同也可加载预训练权重。
+
+```python
+from diffusers import DDPMScheduler, UNet2DModel
+
+scheduler = DDPMScheduler()
+unet = UNet2DModel()
+
+pipeline = UnetSchedulerOneForwardPipeline(unet=unet, scheduler=scheduler)
+output = pipeline()
+# 加载预训练权重
+pipeline = UnetSchedulerOneForwardPipeline.from_pretrained("google/ddpm-cifar10-32", use_safetensors=True)
+output = pipeline()
+```
+
+您可以选择将pipeline作为GitHub社区pipeline或Hub社区pipeline进行分享。
+
+
+
+无论您选择以何种方式贡献,我们都致力于成为一个开放、友好、善良的社区。请阅读我们的[行为准则](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md),并在互动时注意遵守。我们也建议您了解指导本项目的[伦理准则](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/conceptual/ethical_guidelines),并请您遵循同样的透明度和责任原则。
+
+我们高度重视社区的反馈,所以如果您认为自己有能帮助改进库的有价值反馈,请不要犹豫说出来——每条消息、评论、issue和拉取请求(PR)都会被阅读和考虑。
+
+## 概述
+
+您可以通过多种方式做出贡献,从在issue和讨论区回答问题,到向核心库添加新的diffusion模型。
+
+下面我们按难度升序列出不同的贡献方式,所有方式对社区都很有价值:
+
+* 1. 在[Diffusers讨论论坛](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers)或[Discord](https://discord.gg/G7tWnz98XR)上提问和回答问题
+* 2. 在[GitHub Issues标签页](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new/choose)提交新issue,或在[GitHub Discussions标签页](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/discussions/new/choose)发起新讨论
+* 3. 在[GitHub Issues标签页](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues)解答issue,或在[GitHub Discussions标签页](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/discussions)参与讨论
+* 4. 解决标记为"Good first issue"的简单问题,详见[此处](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22good+first+issue%22)
+* 5. 参与[文档](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/docs/source)建设
+* 6. 贡献[社区Pipeline](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3Acommunity-examples)
+* 7. 完善[示例代码](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples)
+* 8. 解决标记为"Good second issue"的中等难度问题,详见[此处](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22Good+second+issue%22)
+* 9. 添加新pipeline/模型/调度器,参见["New Pipeline/Model"](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22New+pipeline%2Fmodel%22)和["New scheduler"](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22New+scheduler%22)类issue。此类贡献请先阅读[设计哲学](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/PHILOSOPHY.md)
+
+重申:**所有贡献对社区都具有重要价值。**下文将详细说明各类贡献方式。
+
+对于4-9类贡献,您需要提交PR(拉取请求),具体操作详见[如何提交PR](#how-to-open-a-pr)章节。
+
+### 1. 在Diffusers讨论区或Discord提问与解答
+
+任何与Diffusers库相关的问题或讨论都可以发布在[官方论坛](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers/)或[Discord频道](https://discord.gg/G7tWnz98XR),包括但不限于:
+- 分享训练/推理实验报告
+- 展示个人项目
+- 咨询非官方训练示例
+- 项目提案
+- 通用反馈
+- 论文解读
+- 基于Diffusers库的个人项目求助
+- 一般性问题
+- 关于diffusion模型的伦理讨论
+- ...
+
+论坛/Discord上的每个问题都能促使社区公开分享知识,很可能帮助未来遇到相同问题的初学者。请务必提出您的疑问。
+同样地,通过回答问题您也在为社区创造公共知识文档,这种贡献极具价值。
+
+**请注意**:提问/回答时投入的精力越多,产生的公共知识质量就越高。精心构建的问题与专业解答能形成高质量知识库,而表述不清的问题则可能降低讨论价值。
+
+低质量的问题或回答会降低公共知识库的整体质量。
+简而言之,高质量的问题或回答应具备*精确性*、*简洁性*、*相关性*、*易于理解*、*可访问性*和*格式规范/表述清晰*等特质。更多详情请参阅[如何提交优质议题](#how-to-write-a-good-issue)章节。
+
+**关于渠道的说明**:
+[*论坛*](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers/63)的内容能被谷歌等搜索引擎更好地收录,且帖子按热度而非时间排序,便于查找历史问答。此外,论坛内容更容易被直接链接引用。
+而*Discord*采用即时聊天模式,适合快速交流。虽然在Discord上可能更快获得解答,但信息会随时间淹没,且难以回溯历史讨论。因此我们强烈建议在论坛发布优质问答,以构建可持续的社区知识库。若Discord讨论产生有价值结论,建议将成果整理发布至论坛以惠及更多读者。
+
+### 2. 在GitHub议题页提交新议题
+
+🧨 Diffusers库的稳健性离不开用户的问题反馈,感谢您的报错。
+
+请注意:GitHub议题仅限处理与Diffusers库代码直接相关的技术问题、错误报告、功能请求或库设计反馈。
+简言之,**与Diffusers库代码(含文档)无关**的内容应发布至[论坛](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers/63)或[Discord](https://discord.gg/G7tWnz98XR)。
+
+**提交新议题时请遵循以下准则**:
+- 确认是否已有类似议题(使用GitHub议题页的搜索栏)
+- 请勿在现有议题下追加新问题。若存在高度关联议题,应新建议题并添加相关链接
+- 确保使用英文提交。非英语用户可通过[DeepL](https://www.deepl.com/translator)等免费工具翻译
+- 检查升级至最新Diffusers版本是否能解决问题。提交前请确认`python -c "import diffusers; print(diffusers.__version__)"`显示的版本号不低于最新版本
+- 记请记住,你在提交新issue时投入的精力越多,得到的回答质量就越高,Diffusers项目的整体issue质量也会越好。
+
+新issue通常包含以下内容:
+
+#### 2.1 可复现的最小化错误报告
+
+错误报告应始终包含可复现的代码片段,并尽可能简洁明了。具体而言:
+- 尽量缩小问题范围,**不要直接粘贴整个代码文件**
+- 规范代码格式
+- 除Diffusers依赖库外,不要包含其他外部库
+- **务必**提供环境信息:可在终端运行`diffusers-cli env`命令,然后将显示的信息复制到issue中
+- 详细说明问题。如果读者不清楚问题所在及其影响,就无法解决问题
+- **确保**读者能以最小成本复现问题。如果代码片段因缺少库或未定义变量而无法运行,读者将无法提供帮助。请确保提供的可复现代码尽可能精简,可直接复制到Python shell运行
+- 如需特定模型/数据集复现问题,请确保读者能获取这些资源。可将模型/数据集上传至[Hub](https://huggingface.co)便于下载。尽量保持模型和数据集体积最小化,降低复现难度
+
+更多信息请参阅[如何撰写优质issue](#how-to-write-a-good-issue)章节。
+
+提交错误报告请点击[此处](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=bug&projects=&template=bug-report.yml)。
+
+#### 2.2 功能请求
+
+优质的功能请求应包含以下要素:
+
+1. 首先说明动机:
+* 是否与库的使用痛点相关?若是,请解释原因,最好提供演示问题的代码片段
+* 是否因项目需求产生?我们很乐意了解详情!
+* 是否是你已实现且认为对社区有价值的功能?请说明它为你解决了什么问题
+2. 用**完整段落**描述功能特性
+3. 提供**代码片段**演示预期用法
+4. 如涉及论文,请附上链接
+5. 可补充任何有助于理解的辅助材料(示意图、截图等)
+
+提交功能请求请点击[此处](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=&template=feature_request.md&title=)。
+
+#### 2.3 设计反馈
+
+关于库设计的反馈(无论正面还是负面)能极大帮助核心维护者打造更友好的库。要了解当前设计理念,请参阅[此文档](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/conceptual/philosophy)如果您认为某个设计选择与当前理念不符,请说明原因及改进建议。如果某个设计选择因过度遵循理念而限制了使用场景,也请解释原因并提出调整方案。
+若某个设计对您特别实用,请同样留下备注——这对未来的设计决策极具参考价值。
+
+您可通过[此链接](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=&template=feedback.md&title=)提交设计反馈。
+
+#### 2.4 技术问题
+
+技术问题主要涉及库代码的实现逻辑或特定功能模块的作用。提问时请务必:
+- 附上相关代码链接
+- 详细说明难以理解的具体原因
+
+技术问题提交入口:[点击此处](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=bug&template=bug-report.yml)
+
+#### 2.5 新模型/调度器/pipeline提案
+
+若diffusion模型社区发布了您希望集成到Diffusers库的新模型、pipeline或调度器,请提供以下信息:
+* 简要说明并附论文或发布链接
+* 开源实现链接(如有)
+* 模型权重下载链接(如已公开)
+
+若您愿意参与开发,请告知我们以便指导。另请尝试通过GitHub账号标记原始组件作者。
+
+提案提交地址:[新建请求](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=New+model%2Fpipeline%2Fscheduler&template=new-model-addition.yml)
+
+### 3. 解答GitHub问题
+
+回答GitHub问题可能需要Diffusers的技术知识,但我们鼓励所有人尝试参与——即使您对答案不完全正确。高质量回答的建议:
+- 保持简洁精炼
+- 严格聚焦问题本身
+- 提供代码/论文等佐证材料
+- 优先用代码说话:若代码片段能解决问题,请提供完整可复现代码
+
+许多问题可能存在离题、重复或无关情况。您可以通过以下方式协助维护者:
+- 引导提问者精确描述问题
+- 标记重复issue并附原链接
+- 推荐用户至[论坛](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers/63)或[Discord](https://discord.gg/G7tWnz98XR)
+
+在确认提交的Bug报告正确且需要修改源代码后,请继续阅读以下章节内容。
+
+以下所有贡献都需要提交PR(拉取请求)。具体操作步骤详见[如何提交PR](#how-to-open-a-pr)章节。
+
+### 4. 修复"Good first issue"类问题
+
+标有[Good first issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22good+first+issue%22)标签的问题通常已说明解决方案建议,便于修复。若该问题尚未关闭且您想尝试解决,只需留言"我想尝试解决这个问题"。通常有三种情况:
+- a.) 问题描述已提出解决方案。若您认可该方案,可直接提交PR或草稿PR进行修复
+- b.) 问题描述未提出解决方案。您可询问修复建议,Diffusers团队会尽快回复。若有成熟解决方案,也可直接提交PR
+- c.) 已有PR但问题未关闭。若原PR停滞,可新开PR并关联原PR(开源社区常见现象)。若PR仍活跃,您可通过建议、审查或协作等方式帮助原作者
+
+### 5. 文档贡献
+
+优秀库**必然**拥有优秀文档!官方文档是新用户的首要接触点,因此文档贡献具有**极高价值**。贡献形式包括:
+- 修正拼写/语法错误
+- 修复文档字符串格式错误(如显示异常或链接失效)
+- 修正文档字符串中张量的形状/维度描述
+- 优化晦涩或错误的说明
+- 更新过时代码示例
+- 文档翻译
+
+[官方文档页面](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/index)所有内容均属可修改范围,对应[文档源文件](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/docs/source)可进行编辑。修改前请查阅[验证说明](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/docs)。
+
+### 6. 贡献社区流程
+
+> [!TIP]
+> 阅读[社区流程](../using-diffusers/custom_pipeline_overview#community-pipelines)指南了解GitHub与Hugging Face Hub社区流程的区别。若想了解我们设立社区流程的原因,请查看GitHub Issue [#841](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/841)(简而言之,我们无法维护diffusion模型所有可能的推理使用方式,但也不希望限制社区构建这些流程)。
+
+贡献社区流程是向社区分享创意与成果的绝佳方式。您可以在[`DiffusionPipeline`]基础上构建流程,任何人都能通过设置`custom_pipeline`参数加载使用。本节将指导您创建一个简单的"单步"流程——UNet仅执行单次前向传播并调用调度器一次。
+
+1. 为社区流程创建one_step_unet.py文件。只要用户已安装相关包,该文件可包含任意所需包。确保仅有一个继承自[`DiffusionPipeline`]的流程类,用于从Hub加载模型权重和调度器配置。在`__init__`函数中添加UNet和调度器。
+
+ 同时添加`register_modules`函数,确保您的流程及其组件可通过[`~DiffusionPipeline.save_pretrained`]保存。
+
+```py
+from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
+import torch
+
+class UnetSchedulerOneForwardPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
+ def __init__(self, unet, scheduler):
+ super().__init__()
+
+ self.register_modules(unet=unet, scheduler=scheduler)
+```
+
+2. 在前向传播中(建议定义为`__call__`),可添加任意功能。对于"单步"流程,创建随机图像并通过设置`timestep=1`调用UNet和调度器一次。
+
+```py
+ from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
+ import torch
+
+ class UnetSchedulerOneForwardPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
+ def __init__(self, unet, scheduler):
+ super().__init__()
+
+ self.register_modules(unet=unet, scheduler=scheduler)
+
+ def __call__(self):
+ image = torch.randn(
+ (1, self.unet.config.in_channels, self.unet.config.sample_size, self.unet.config.sample_size),
+ )
+ timestep = 1
+
+ model_output = self.unet(image, timestep).sample
+ scheduler_output = self.scheduler.step(model_output, timestep, image).prev_sample
+
+ return scheduler_output
+```
+
+现在您可以通过传入UNet和调度器来运行流程,若流程结构相同也可加载预训练权重。
+
+```python
+from diffusers import DDPMScheduler, UNet2DModel
+
+scheduler = DDPMScheduler()
+unet = UNet2DModel()
+
+pipeline = UnetSchedulerOneForwardPipeline(unet=unet, scheduler=scheduler)
+output = pipeline()
+# 加载预训练权重
+pipeline = UnetSchedulerOneForwardPipeline.from_pretrained("google/ddpm-cifar10-32", use_safetensors=True)
+output = pipeline()
+```
+
+您可以选择将pipeline作为GitHub社区pipeline或Hub社区pipeline进行分享。
+
+